What is AI dubbing and how does it differ from TTS and voiceover?
Core technical components
-
Voice cloning: creates a model that mimics a real speaker’s timbre and phrasing. Useful for brand consistency.
-
Alignment: maps audio to video frames so lines start and end where the speaker’s mouth moves. This is subtitle timing plus lip-syncing.
-
Translation: converts the source script into target languages while keeping meaning and timing.
-
Subtitle sync: generates SRT or captions that match the new audio, including reading speed and line breaks.
When dubbing beats subtitles
Why AI dubbing matters for e-learning courses
Key benefits for L&D teams
-
Higher engagement and completion: Native-language narration keeps learners focused. Short, natural-sounding audio increases watch time and course completion.
-
Better accessibility and inclusion: Dubbing adds audio for learners with low literacy or visual impairment. Paired with accurate subtitles, it meets more accessibility standards.
-
Faster time to localize: Automated voice cloning and subtitle alignment cut weeks from the localization cycle. Teams can roll out translated audio in hours, not days.
-
Lower per-course cost at scale: After initial setup, incremental costs fall dramatically. Reusing cloned voices and automated workflows reduces human recording and studio fees.
Metrics to track and why they matter
-
Completion rate: Higher completions show content fits the audience. Dubbing should move this number up within weeks.
-
Retention and replay rate: More replays or lower dropout means learners understand and prefer the localized version.
-
Learner satisfaction (CSAT or NPS): Qualitative feedback shows perceived quality and cultural fit.
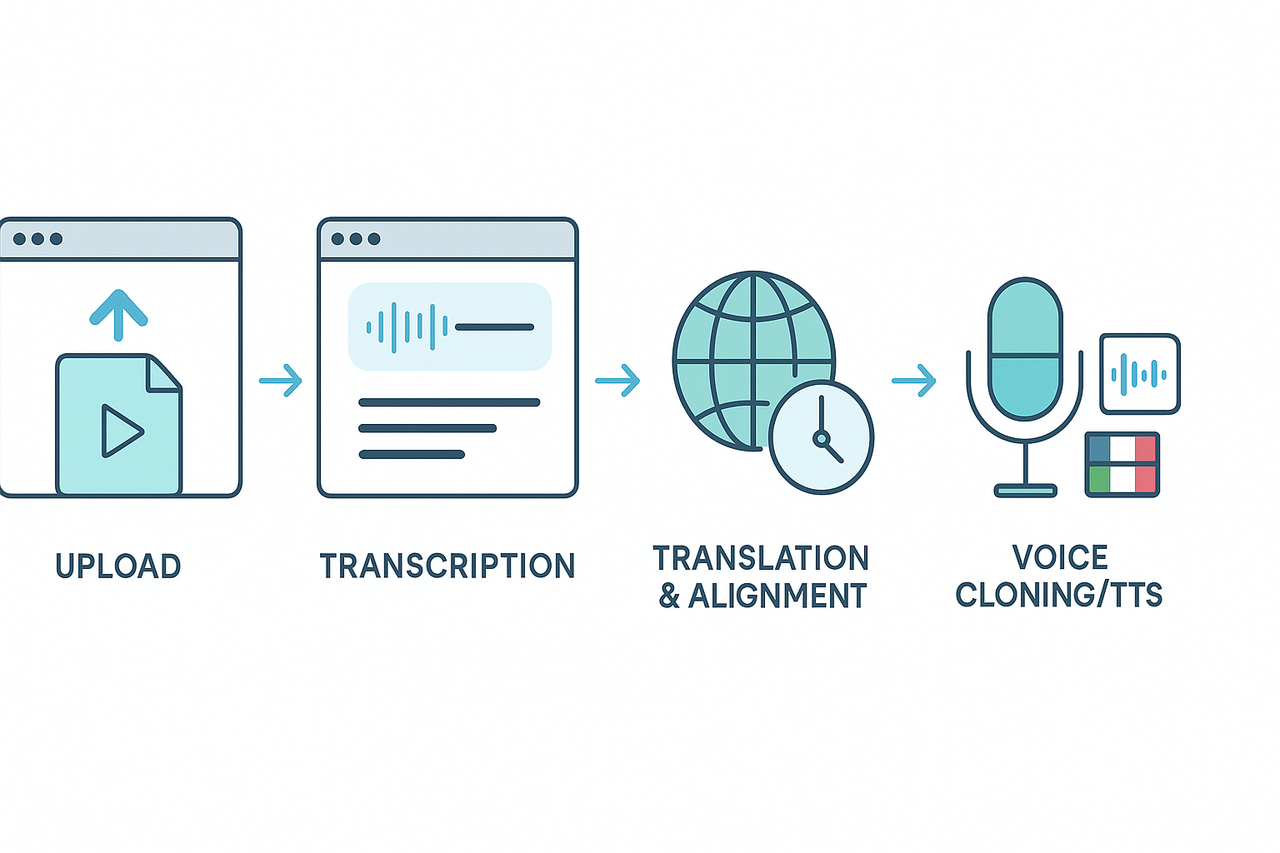
How DupDub’s End-to-End AI Dubbing Workflow Works
1. Upload and Ingest
-
Upload a video/audio file or attach an existing transcript.
-
Platform extracts timeline metadata and thumbnails.
-
Files are stored and preprocessed for individual or batch processing.
2. Auto-Transcription
-
Speech-to-text engines generate a time-coded transcript.
-
Automatic subtitles are created.
-
Editors can review and modify the transcript inline.
3. Voice Cloning and TTS Voice Selection
-
Choose a synthetic or cloned voice from DupDub’s library.
-
Preview styles and emotional tones.
-
Apply voice profiles for consistent branding across content.
4. Translation and Subtitle Alignment
-
Translate the transcript into the target language automatically.
-
Adjust subtitle timing to match speech cadence and mouth movements.
-
For low-latency uses, platforms like StreamSpeech achieve sub-300ms latency on consumer hardware (source).
5. Export and Review
-
Render dubbed audio tracks with optional burned-in or soft subtitles.
-
Generate final MP4 previews for review.
-
QA ensures timing and tone accuracy before download.
Export Formats:
-
MP4: video with dubbed audio and subtitles
-
MP3: audio track for audio-only platforms
-
SRT: subtitle tracks for LMS or player integration
Automation & APIs
Prep checklist
-
Source files: final videos, master audio, and editable transcripts (SRT or TXT). Keep originals for fallback.
-
Style guide: tone, pace (wpm), pronunciation notes, and brand voice rules.
-
Glossary: product names, proper nouns, acronyms, and preferred translations.
-
Accessibility specs: caption formatting and color/position rules.
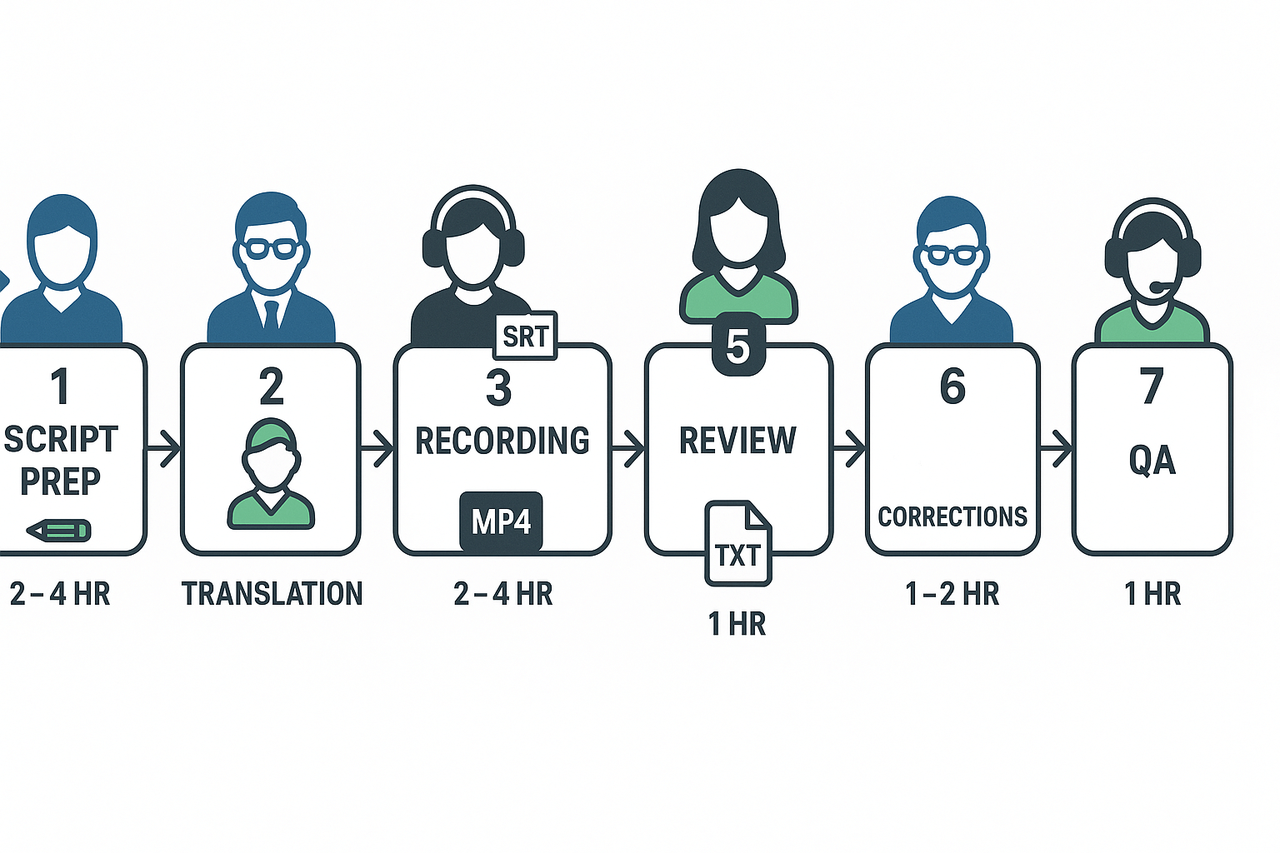
Seven-step workflow (roles and timings)
-
Script cleanup and timestamping (Instructional designer, 2–4 hrs per lesson): finalize transcript and mark timing.
-
Voice selection or clone setup (Localization lead, 1–2 hrs): pick voice, accent, and energy.
-
Machine translation and draft subtitles (Translator + tool, 1–3 hrs): generate captions and align to timing.
-
AI dubbing pass (Multimedia producer, 10–40 min per lesson): synthesize voiceover and produce dubbed MP4/MP3.
-
In-house review (Subject matter expert, 1–2 hrs): check terminology and tone.
-
QA and accessibility check (QA lead, 30–60 min): watch for sync, audio levels, and captions.
-
Final edits and export (Producer, 30–90 min): apply fixes, version, and deliver assets.
QA, versioning, and a sample sprint plan
-
Follow accessibility rules: Understanding Success Criterion 1.2.2: Captions (Prerecorded) requires that captions be provided for all prerecorded audio content in synchronized media.
-
Check lip-sync tolerance and clip start/end trims.
-
Use listeners in target locales for a subjective pass.
-
Keep source_master_v1, dubbed_lang_v1, and qa_lang_v1. Include changelogs.
-
Week 1: Scripts cleaned and voices chosen; translations started.
-
Week 2: Dubbing, QA, and final exports. Team estimate: 1 localization lead, 1 producer, 1 QA, plus SMEs as needed. This pilot finds issues fast and produces a clear ROI signal for scaling.
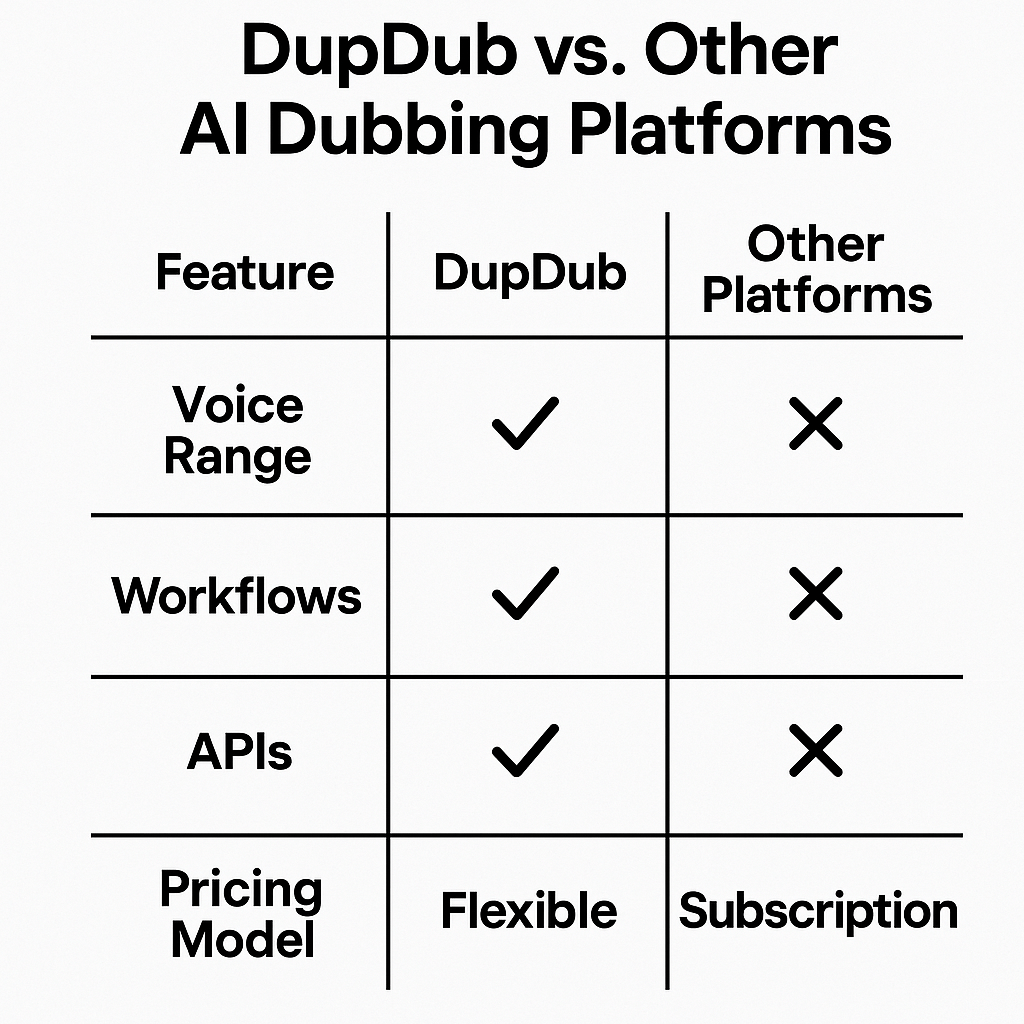
Comparison: DupDub vs. other AI dubbing solutions
Feature snapshot
|
Dimension
|
DupDub
|
Typical competitor types
|
|
Voices & languages
|
700+ voices, 90+ TTS languages, 47-language cloning
|
TTS-only vendors: large voice catalogs but fewer clones; Boutique labs: premium clones, limited languages
|
|
End-to-end workflow
|
Built-in subtitles, alignment, video export
|
Fragmented tools, manual stitching required
|
|
Integrations & API
|
API, Canva, YouTube plugin, automation
|
Varies: some offer APIs, many need custom work
|
|
Pricing model
|
Credit-based free trial, tiered subscriptions
|
Per-minute or project pricing; enterprise quotes common
|
|
Security & privacy
|
Encrypted voice data, user-only cloning
|
Policies vary; check retention and reuse terms
|
Which vendor fits your use case
-
Use DupDub when you need one tool for voice, subtitles, and translation, and fast proof-of-concept work. It scales from single creators to teams.
-
Pick TTS specialists if you want the widest voice realism for a single language at low cost.
-
Choose boutique cloning studios for ultra-high fidelity, bespoke rights, and governed enterprise SLAs.
-
DupDub pros: integrated workflow, language breadth, fast iteration.
-
DupDub cons: credit-based limits may need planning for bulk projects.
Mini case study: Localizing a 60-minute course — results & ROI
Project goals and baseline
Workflow used
-
Upload original MP4 and source script.
-
Auto-transcribe and generate aligned subtitles.
-
Translate subtitles and on-screen text with review.
-
Produce voice clones and synthetic narration per language.
-
Integrate audio, apply minor timing edits, export MP4 and SRT.
Key outcomes and ROI
-
Time to localize one language dropped from roughly 40 hours to about 6 hours, an 85% reduction.
-
Localization cost fell by roughly 70% per language.
-
Course completion rate rose from 52% to 62% after localization.
-
Learner satisfaction comments shifted from “hard to follow” to “natural and clear.”
Lessons learned
Best practices, limitations, and ethical considerations
Get explicit consent and protect voice data
Check cultural accuracy and tone
When to require human review
Technical limitations and how to mitigate
-
Noisy source audio: clean or re-record before cloning.
-
Tight timing or music beds: edit timing manually in a DAW or video editor.
-
Rare languages or accents: pair AI output with a native voice actor for final pass.
-
Lip sync for talking heads: use subtitle-first delivery or manual animation tweaks.
FAQ — People Also Ask & common implementation questions
-
How accurate is AI dubbing for e-learning courses?
Accuracy depends on script clarity, audio quality, and the language pair. Modern AI dubbing can deliver near-human clarity for clear, well-edited scripts, but you should still plan a human review pass for tone and timing. Run a 5-minute pilot and measure learner comprehension. Try the DupDub 3-day free trial and use the downloadable quick-start checklist to validate results on your courses.
-
What is the voice cloning process and consent for e-learning dubbing AI?
Voice cloning trains a model from recorded samples (usually minutes of speech). You must get written consent, store consent records, and only clone voices with explicit permission. Platforms often require verification and encrypt voice data. Keep consent forms and samples with your training assets for audits.
-
Which languages and file formats does e-learning dubbing AI support?
Most tools support dozens of languages for TTS and subtitle extraction. Common export formats are MP3, WAV for audio, MP4 for video, and SRT for subtitles (editable subtitle files). Confirm the platform can export editable SRTs so your LMS or captioning tool can ingest them.
-
Turnaround and pricing models for e-learning dubbing AI
Short clips can be dubbed in minutes, full lessons in hours, and large localization projects in days. Pricing varies: per-minute, credit-based, or subscription tiers with enterprise quotes. Compare API docs, ingestion limits, and pricing pages before committing to a vendor.
-
How does AI dubbing accessibility for e-learning courses handle captions and compliance?
AI dubbing usually creates time-aligned subtitles, which help accessibility and search. For compliance, always review and correct automated captions to ensure verbatim accuracy. Export editable captions and keep the original audio track for users who need it.

