TL;DR: Quick answer: When to pick AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing
When comparing AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing, choose AI when speed and scale matter. AI dubbing drops per-video cost and cuts turnaround from days or weeks to hours. It fits rapid social clips, course updates, and large catalog localization. Quality for many languages is now very close to human.
Go human when performance and nuance drive results. Use human dubbing for commercials, film, or any creative work where emotion sells. Actors deliver natural timing, cultural adaptation, and authentic lip-sync for close-ups. They also adapt jokes, idioms, and cultural tone.
Expect trade-offs: AI gives consistency, fast iteration, and easy A/B testing. Humans give interpretive choices, precise voice direction, and legal confidence for regulated scripts. Hybrid workflows blend both: AI for drafts, humans for final polish. AI is great for fast tests, not always for nuance.
Quick rule of thumb: pick AI for volume, speed, and cost efficiency. Pick traditional for flagship assets, tight brand control, or legally sensitive material. If unsure, run a small pilot to compare cost, time, and perceived quality. A quick pilot reveals real audience reaction and cost per view.
Why the choice matters: impact on reach, cost, and brand
Choosing between AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing changes how your content performs and how fast it ships. The method you pick affects who sees your video, how much each language costs, and whether your brand still sounds like your brand. These trade-offs decide reach, localization ROI, and long-term trust.
Reach and audience expectations
Dubbing widens reach by making content native to each market. Viewers prefer a voice that feels natural for their culture and platform. Fast-paced channels and short-form formats often favor quick AI dubs to scale reach rapidly.
Per-language cost and scale
Traditional dubbing pays for actors, studio time, direction, and revisions. Those costs grow with each target language. AI tools can lower marginal cost per language, and platforms with credit models help predict spend. For example, many teams compare traditional vendor bids to DupDub's tiered credits to model savings at scale.
Brand voice fidelity and trust
A consistent brand voice boosts recognition and trust across markets. Human actors still win on nuance and star power. AI cloning narrows that gap, but it needs careful tuning to match tone, emotion, and pacing.
Measurable business outcomes
Measure what matters: views, watch time, completion rate, cost per acquisition, and time to market. Track localization ROI by comparing incremental reach and conversion lift. Use A/B tests to pick human, AI, or hybrid workflows for each campaign.
How AI dubbing actually works, a technical but approachable deep dive
This section breaks down the core AI blocks behind modern dubbing and why results differ between ai dubbing vs traditional dubbing. You will get a clear view of the pipeline, the typical errors at each step, and why human review remains important for broadcast quality.
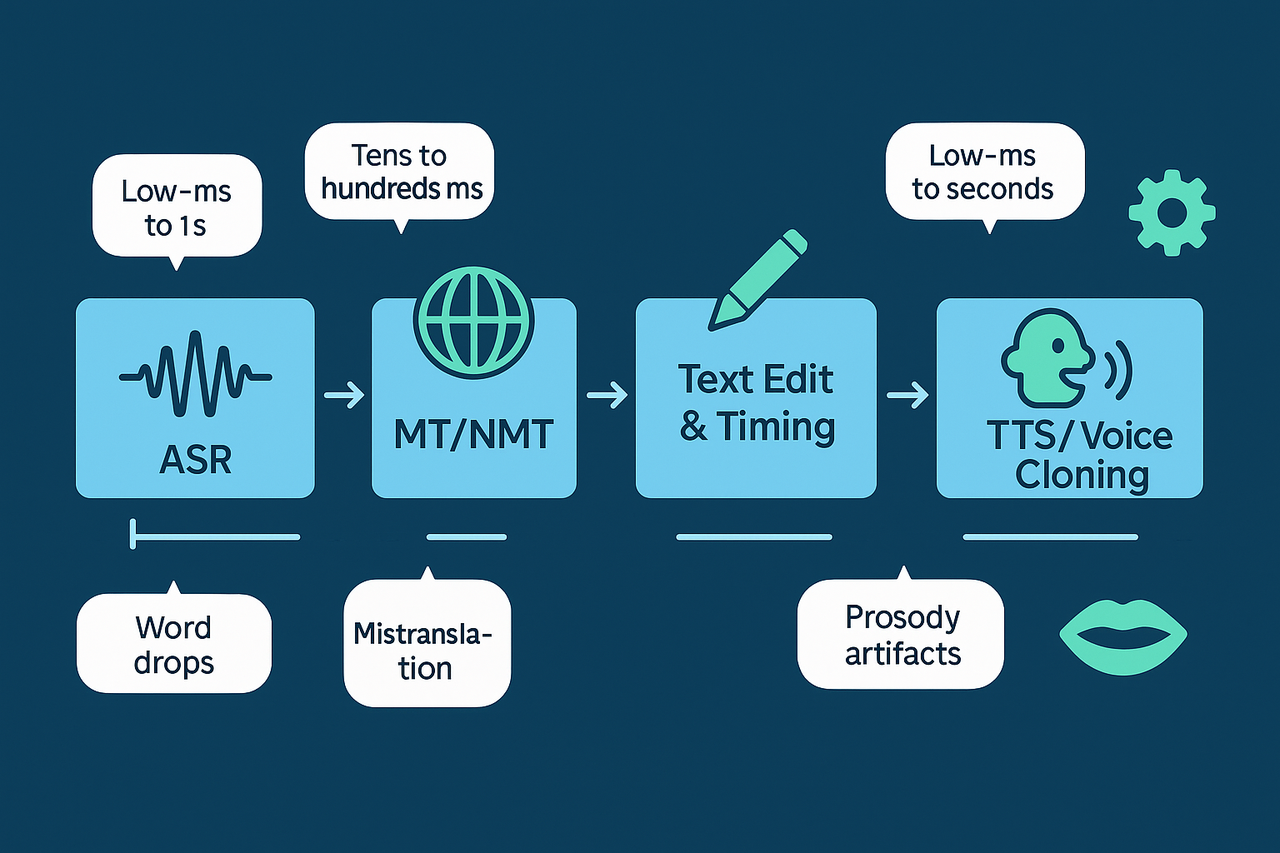
Core pipeline, step by step
-
-
Machine translation (MT/NMT): The transcript is translated into the target language using neural machine translation. Modern NMT captures context, but it can mistranslate idioms, brand names, or short clips out of context. Post-editing is often required.
-
Text edit and timing: Editors fix mistranslations, length, and cultural references. Timing constraints are set so the translated text fits the original speech duration or allowed expansion.
-
Text to speech and voice cloning (TTS): TTS renders the translated text into audio. Voice cloning recreates a voice timbre using a short sample of the original speaker. High-quality cloned voices keep brand consistency, but small prosody errors or unnatural breaths can reveal synthetic audio.
-
Lip-sync and timing layer: Algorithms shift phoneme timing to match mouth movements and scene cuts. Good lip-sync reduces viewer distraction, but perfect lip match is hard for close-ups and expressive speakers.
Where systems fail, and how to catch them early
-
ASR: word substitutions, dropped words in noisy or overlapped speech.
-
MT: literal translations, wrong register, misspelled named entities.
-
TTS/clone: robotic cadence, breath placement errors, incorrect stress.
-
Lip-sync: off-timed phonemes, mismatched pauses around mouth movements.
Automated checks catch many issues: word error rate thresholds, bilingual alignment mismatches, and waveform similarity metrics. Still, human-in-the-loop QA is crucial for tone, legal accuracy, and brand voice.
Quick checklist for quality
-
Verify ASR timestamps and confidence scores.
-
Use bilingual editors for MT post-editing.
-
Listen for unnatural prosody and test on-device playback.
-
Run a final visual sync pass on the target video.
Clone your voice in minutes.
Traditional dubbing workflow: step-by-step (what agencies do)
This section lays out the full agency-style pipeline for human dubbing. It contrasts roles, hours, and costs so you can compare AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing. Expect a clear view of where humans add value and where automation can speed work.
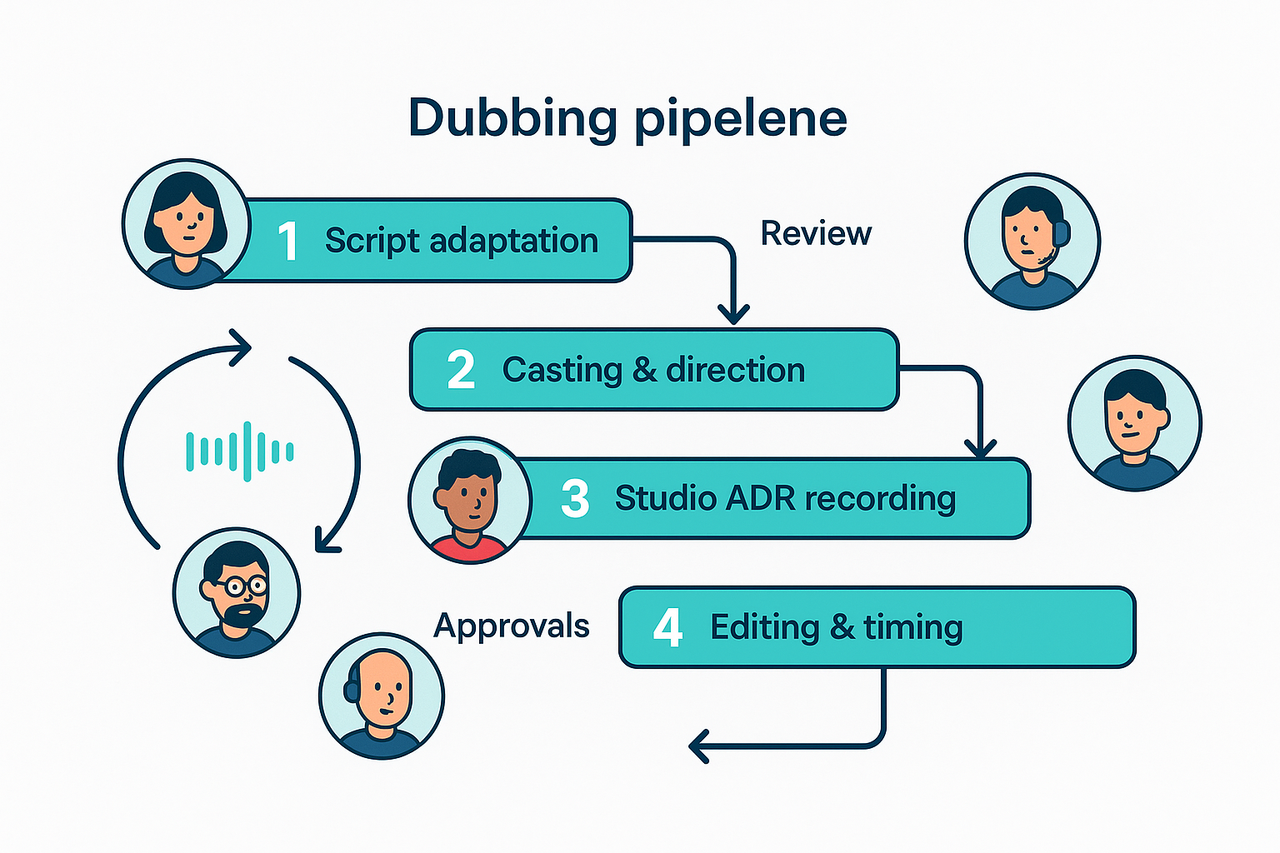
1) Script localization and adaptation
Translators turn literal text into natural dialogue. A localization writer adapts jokes, idioms, and timing to match local culture. This step often needs pass edits with the director to keep lip and mouth timing. It usually takes one to three hours per finished minute of video.
2) Casting and direction
Casting finds voices that match the original tone and the brand. Casting directors run auditions, shortlist actors, and schedule sessions. The director defines performance notes and reference takes. Casting can take days and adds per-actor fees and audition costs.
3) Studio ADR recording
ADR (automated dialogue replacement, the studio re-recording) is where actors record to picture. A voice director coaches performance while an engineer captures clean audio. Sessions include multiple retakes and pickups, so studio time and actor fees add up fast. Expect two to five hours of studio work per finished minute.
4) Editing and timing
Dialogue editors clean noise, align takes, and match timing to lips. Editors compile alternate takes and solve sync issues, then hand files to the mixer. The platform DupDub can produce rough alignments and subtitle files to speed reviews, but a human editor still polishes the performance. Editing often takes one to three hours per finished minute.
5) Final mix and delivery
A re-recording mixer balances levels, adds room tone, and integrates SFX and music. The team runs QA checks, reviews on-device playback, and prepares masters for each platform. Final exports include stems, closed captions, and delivery notes for distribution.
Estimated time and people costs (typical ranges):
-
Script adaptation: 0.5–3 hours per minute, 1–2 specialists.
-
Casting: 2–10 days, casting fees plus per-actor rates.
-
Studio ADR: 2–5 hours per minute, studio $/hour and actor session fees.
-
Editing: 1–3 hours per minute, 1 editor.
-
Mixing and QA: 1–2 hours per minute, mixer and QA lead.
This pipeline shows where AI cuts time: quick rough drafts, subtitle alignment, and initial voice matches. It also shows human-only value: nuanced acting, creative direction, and final quality control.
Cost comparison: dubbing pricing explained (real examples + DupDub math)
The total cost of localization depends on choices and scale. This section compares AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing and shows where the money goes. It gives worked numbers you can copy into the downloadable pricing calculator.
Primary cost drivers
There are four buckets you should always model. Each drives the final price and time to market:
-
Talent fees: voice actors, casting, and buyouts for reuse.
-
Studio time and equipment: recording rooms, engineers, and ADR when lips must match.
-
Project management and localization: script adaptation, direction, and review rounds.
-
Post-production: editing, mixing, QC, and final mastering.
These line items stack up for human dubbing. An AI-first workflow shifts most costs into software credits, QA, and minimal human editing.
Worked examples: human dubbing versus AI-first (DupDub math)
Assumptions used:
-
Credits per minute = 1.2 (based on product credit bundles)
-
Professional Plan: $30 for 500 credits
-
Ultimate Plan: $110 for 2,500 credits
Human rates are conservative; AI costs are broken down explicitly.
|
Scenario
|
Duration
|
Human Cost (USD)
|
AI-first Cost (USD)
|
|
Short social clip
|
1 min
|
Talent $$300 + Studio$$200 + PM/Post $$250 =$$750
|
Credits: 1.2 (Pro plan $$0.06/credit) ≈$$0.07 + Human editor $$30 = *$$40**
|
|
Multi-hour e-learning
|
10 hrs
|
Narration+Editing $$400/hr =$$4,000; PM $$2,000 = *$$6,000**
|
600 mins × 1.2 = 720 credits → $$32 (Ultimate plan) + QA/Edit:$$900 = $932
|
|
Feature-length film
|
100 mins
|
Multi-actor ADR, legal = $80,000
|
Credits: 120 → $$5 + Direction/ADR QA$$12,000 = $12,005
|
How to use this table
-
Adjust credit-per-minute values if your provider differs. Use 1.2 as a baseline.
-
Compute per-credit pricing based on your subscription plan.
-
Add human QA/editing estimates: 5–15 min QA per hour of dubbed audio is typical. Use your editor's rate to estimate.
AI-first dubbing dramatically reduces talent and studio costs. Human review becomes the key scaling consideration. Use these worked examples to model savings and tradeoffs.
Time, scale & workflows: how each approach affects project timelines
When comparing AI dubbing to traditional dubbing, timelines and scalability often determine which approach wins. According to
Rethinking Localization In The Age Of AI, traditional localization methods can obstruct global growth, necessitating modern solutions.
Typical turnaround times
Traditional dubbing involves several stages—script adaptation, casting, recording, editing, and QA. A 3–7 minute video typically takes 3–14 business days per language. For extensive content like e-learning modules, this can stretch to 2–4 weeks per language.
AI-driven dubbing accelerates the process. Automated transcription, machine translation, and text-to-speech (TTS) can create a draft voiceover in minutes. With a human reviewer involved, final output is often delivered within 24–72 hours per language.
Approximate task durations:
-
Script translation & glossary work: 1–5 days (human), or hours (AI-assisted)
-
Voice casting & recording: 1–7 days (human), or instant (AI)
-
Editing & sync: 1–5 days (human), or minutes (AI)
Scaling to 10–20+ languages
Human-centric workflows scale linearly: more languages mean higher costs and longer durations due to casting, recording, and QA dependencies. AI-centric workflows scale in parallel—content is generated simultaneously across many languages, bottlenecked only by review and QA.
Tips for scaling:
-
Group similar content types to reuse assets like glossaries.
-
Focus human review on the top-priority languages.
-
Use automation tools to manage subtitles and media assets.
Project management evolution
Scaling introduces complexity:
-
Traditional workflows require coordination with voice actors, studios, and vendors.
-
AI workflows require managing voice models and automated toolchains.
Both need clear sign-off processes, though human workflows lean heavily on linguists, while AI workflows focus on engineers and quality reviewers.
Hybrid workflows that maximize efficiency
Many teams now embrace a hybrid strategy:
-
Auto-generate transcripts, translations, and sync via AI.
-
Create AI voice dubs for all languages.
-
Assign human review/polish to top-tier locales.
-
Final quality checks and publish.
This approach reduces dependence on studios, allowing faster turnaround and resource optimization.
Want to localize at scale? Consider hybrid dubbing to save time while maintaining quality.
Quality, creative control, legal & ethical considerations
Choosing between AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing affects more than price. It also shapes emotional nuance, approval loops, and legal risk. This section shows what you gain and what you trade off when you pick AI or human voice actors.
Preserve emotional nuance and brand voice
Human dubbing gives natural emotion, timing, and improvisation. That matters for branded spots and character-driven stories. AI dubbing can match tone, speed up iterations, and keep voice consistency across languages. But it may struggle with subtle breath timing, comic timing, or unscripted ad-libs. Plan a creative approval loop: script review, test renders, and a final signoff from brand voice owners. That workflow reduces rework whether you use talent or synthetic voices.
Creative control: workflows that work
Use a hybrid approach for best results. Example steps:
-
Start with AI drafts to proofread pace and localization.
-
Replace key lines with human takes for emotional beats.
-
Run a final audio pass for lip-sync and accents. This keeps costs down and preserves craft where it matters. Also, lock a single source of truth for the script and subtitles to avoid version drift in dubbing workflows.
Legal and ethical checklist
Be careful with voice rights, consent, and data handling. Importantly,
Process personal data lawfully notes: The processing of biometric data, such as voice data used for voice cloning, is generally prohibited under the GDPR unless the individual has given their explicit consent. That rule means you must document consent for any cloned voice. Also verify:
-
Written release from voice talent for use and reuse.
-
Contract clauses for moral rights and geography.
-
Copyright clearance for translated scripts and music beds.
-
Clear retention policies and secure storage for voice files.
Short note on enterprise safeguards DupDub enforces consent checks, encrypted storage, and a policy that only originals can upload voices for cloning. The platform also offers audit logs and data deletion controls to align with procurement and privacy reviews. Ask vendors for sample consent language and a data processing agreement during procurement.
Decision matrix & recommended use-cases (industry-specific guidance)
This matrix helps you pick between AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing based on business needs, content type, and risk tolerance. Use the table to match priorities to an approach: AI-only, human-only, or a hybrid that mixes both.
Decision matrix at a glance
|
Need or content type
|
Priority factors
|
Recommended approach
|
|
Short social clips, low budget
|
Speed, cost, many languages
|
AI-only
|
|
High-volume e-learning
|
Consistency, scale, glossary control
|
Hybrid (AI for base, human QA)
|
|
Branded creative film or TV
|
Emotional nuance, lip-sync, casting
|
Human-only
|
|
Confidential internal comms
|
Privacy, legal review, speaker identity
|
Human-only or secure hybrid
|
|
Performance ads, voice talent critical
|
Casting, brand voice, A/B testing
|
Human-first with AI for variants
|
Industry-specific guidance
Marketing: Use AI-first for multilingual social and product explainers. For hero campaigns, hire actors and use human dubbing for lip-sync and casting. AI can speed up multivariate ad tests.
E-learning: For thousands of modules, combine an AI engine for base narration with human editors for technical accuracy. For scalable voice cloning and enterprise privacy, consider a platform like DupDub to keep voices consistent across courses.
Film and TV: Choose human dubbing when performance matters. Use hybrid workflows only for temp tracks or early localization, then recast and re-record for final delivery.
Internal communications: Prioritize security and native-speaker moderators. Use human recording when legal or HR content is sensitive. AI can help translate and draft subtitles quickly.
Ads and performance creatives: Speed matters, but brand voice is vital. Start with AI for rapid iterations, then replace winners with human talent for final cuts.
Quick project scoring checklist
-
Timeline: Tight (2) or flexible (0)
-
Budget: Low (2) or ample (0)
-
Need for nuance: High (0) or low (2)
-
Scale (languages/minutes): Large (2) or small (0)
-
Privacy/legal risk: High (0) or low (2)
Score 0–3: Human-first. Score 4–7: Hybrid. Score 8–10: AI-only. Use this to pick resources and plan QA steps.
How to run a pilot with DupDub — step-by-step pilot plan + metrics to track
Run a focused pilot to compare AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing and prove ROI fast. Use a small sample set and clear success metrics. DupDub makes it simple to test multiple languages, voice clones, and A/B audio samples.
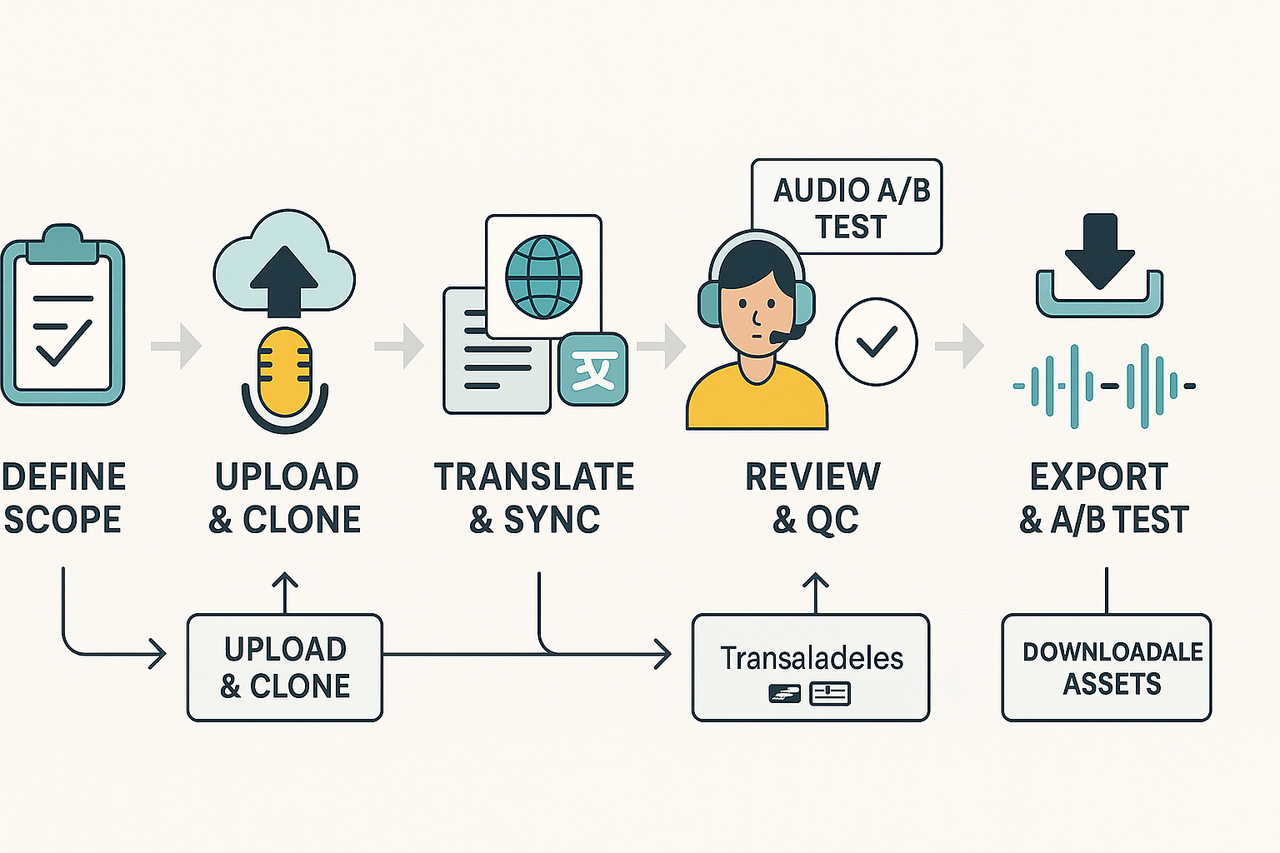
Set goals and scope
Pick 3 to 5 videos that represent your content types. Define success metrics, for example cost per language, time per asset, and engagement lift. Limit languages to two high-value markets for the first run.
Upload assets and clone voices
Upload source files and transcripts, or let the platform create captions automatically. Create one clone of the original speaker for brand consistency, or pick a neutral AI voice. Tag each asset with language and target audience to keep the pilot organized.
Translate, sync, and generate dubs
Run machine translation for scripts, then apply neural TTS (text to speech) or cloned voices. Use subtitle alignment to sync audio with on-screen text. Export quick drafts for internal listening within minutes.
Schedule human QC passes and reviews
Plan two review rounds: linguistic QA, then creative QA. Assign short tasks to reviewers, like timecode notes and a single correction list per round. Track fixes in a shared sheet to measure error rate.
Export, run A/B tests, and measure
Export MP4, MP3, and SRT files for each language variant. Run A/B tests on a subset of your audience to compare human versus AI voice. Use the same thumbnail and copy to isolate audio impact.
Metrics to track
-
Cost per language: total pilot spend divided by languages tested. Include credits, human review hours, and platform fees.
-
Time per language: hours from upload to final export.
-
Time saved: compare against typical agency timelines.
-
Engagement lift: view rate, watch time, and CTR differences between variants.
-
QA correction rate: number of edits per minute of video.
-
Throughput: final deliverables per week.
Mini case study: e-learning pilot
A 12-video course ran a two-week pilot with two target languages. The team cloned the instructor voice, produced dubs, and ran one QC pass. They cut per-language cost by 65% and time to publish from three weeks to four days. Engagement rose 18% in the new markets.
FAQ — common questions about AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing
-
Can AI match human emotion in voiceovers for AI dubbing vs traditional dubbing?
AI can reproduce tone and timing well. Modern voice cloning and expressive TTS add emotion and style. For high-sensitivity creative spots, human actors still lead. For eLearning, ads at scale, or bulk localization, AI often hits the mark.
-
Is voice cloning legal and safe for dubbing pricing and IP use?
Voice cloning is legal when you have consent and clear rights. Use written releases for talent and check local law. Secure vendors, keep encryption, and require deletion or limited retention clauses.
-
How realistic are localization costs and dubbing pricing for enterprise projects?
Human dubbing often costs hundreds to thousands per finished minute. AI dubbing can cut that to single or low double digits per minute depending on features. For reference, subscription tiers start at $11, and higher tiers give more voice hours and credits.
-
What are the accessibility implications when localizing for deaf or low-vision users?
Good localization improves accessibility: accurate captions, speaker labels, and multiple audio tracks matter. Auto-generated captions need human review for compliance and clarity.
-
What vendor selection criteria should I use for dubbing workflows?
Rank vendors by voice quality, language coverage, turnaround, API and CMS integration, security, and pricing model. Ask for A/B samples, case studies, and references.
-
Can AI handle lip-sync and cultural nuance in dubbing workflows?
AI can auto lip-sync and match timing well for many formats. Cultural nuance, slang, and idioms often need human post-editing.
-
What metrics should I track during a DupDub pilot or dubbing pilot?
Track cost per language, time per minute, quality score from reviewers, engagement lift, and error rate. Include A/B listening tests and accessibility checks.