-
Confirm speaker consent and usage rights in writing, with revocation options.
-
Run a cultural adaptation review with native reviewers for each target market.
-
Add human-in-the-loop checkpoints: script sign-off, pre-release audio checks, and content veto rights.
-
Log provenance and secure voice data, so you can audit decisions later.
Why an AI localization ethics code matters now
Common localization risks
-
Mistranslation of cultural signals. Literal translations miss tone, humor, or taboos.
-
Unauthorized voice use. Cloning a voice without consent harms trust.
-
Brand reputation damage. Wrong voice or phrasing can alienate audiences.
-
Legal and privacy gaps. Contracts, rights, and consent vary by market.
Business risks: why write it down
Principles of culturally sensitive AI localization (core ethics)
Respect local context: center audience dignity and norms
-
Verify honorifics and formality levels in the translated script.
-
Review visual cues and gestures for regional meaning.
-
Confirm that humor, idioms, and references map to local equivalents.
Require robust consent and voice cloning safety
-
Collect signed consent that describes languages and distribution channels.
-
Store voice models with role-based access and encryption.
-
Preserve originals and deletion records for audits.
Mandate transparency, labels, and explainable logs
-
Add audible or visual tags noting synthetic audio.
-
Maintain versioned logs for model updates and edits.
-
Run periodic audits to verify labels and consent.
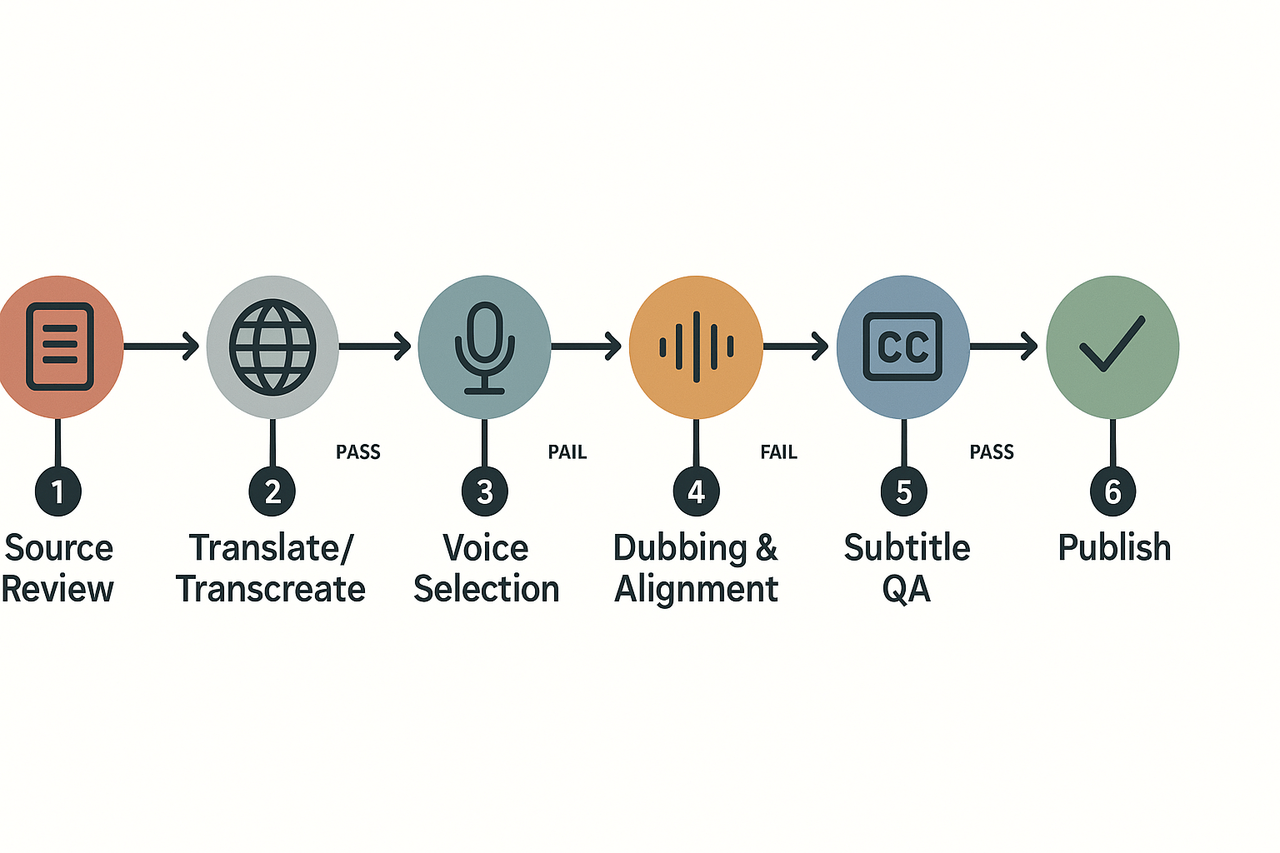
Cultural adaptation checklist — practical items for each stage
How to use this checklist
1) Source content review
-
Is the source script free of culturally loaded terms or stereotypes? Pass if no flagged language remains.
-
Are visual cues or gestures tagged for regional review? Pass if all cues have a region flag or explanation.
-
Does the source contain political or religious references? Fail if unresolved; route to subject-matter reviewer.
2) Translation and transcreation checks
-
Does the translation preserve intent and tone, not just literal text? Pass if the reviewer confirms the intent match.
-
Is idiomatic language adapted for the target culture? Pass if transcreation examples are approved.
-
Are any brand names, humor, or metaphors flagged for alternative phrasing? Fail if no safe alternative is provided.
3) Voice selection and persona alignment
-
Does the selected voice match the brand persona and target audience? Pass if the persona checklist matches the voice attributes.
-
Is a human actor required due to sensitivity or legal consent? Fail if a synthetic voice is used without documented consent.
-
Are accents and dialect choices respectful and accurate? Pass if checked by a native reviewer.
4) Dubbing, timing, and alignment
-
Is lip sync and timing natural for the target language? Pass if alignment deviation is within set seconds.
-
Are emotional cues matched to the scene? Fail if tone conflicts with on-screen expression.
-
Are local sound cues or SFX culturally appropriate? Pass if SFX reviewer signs off.
5) Subtitle timing and readability
-
Are subtitles readable and within length limits per language? Pass if 2-line max and 1.5 seconds minimum reading time.
-
Do subtitles avoid literal translations that change meaning? Fail if mistranslation alters intent.
6) Multimodal checks for gestures and avatars
-
Do avatar gestures match regional norms? Pass if gestures are reviewed by a cultural consultant.
-
Is the avatar clothing and background context appropriate? Fail if any element could offend.
Reviewers, flags, and remediation
-
Assign one linguistic reviewer, one cultural consultant, and one legal/compliance reviewer per region.
-
Add a regional sensitivity flag when any item fails. Route failed items to the assigned reviewer with a 48-hour SLA.
Human versus synthetic voice rules
-
Use human actors when legal consent, speaker identity, or sensitive topics are involved.
-
Use synthetic voices for high-volume, low-risk content or where consent and likeness controls exist.
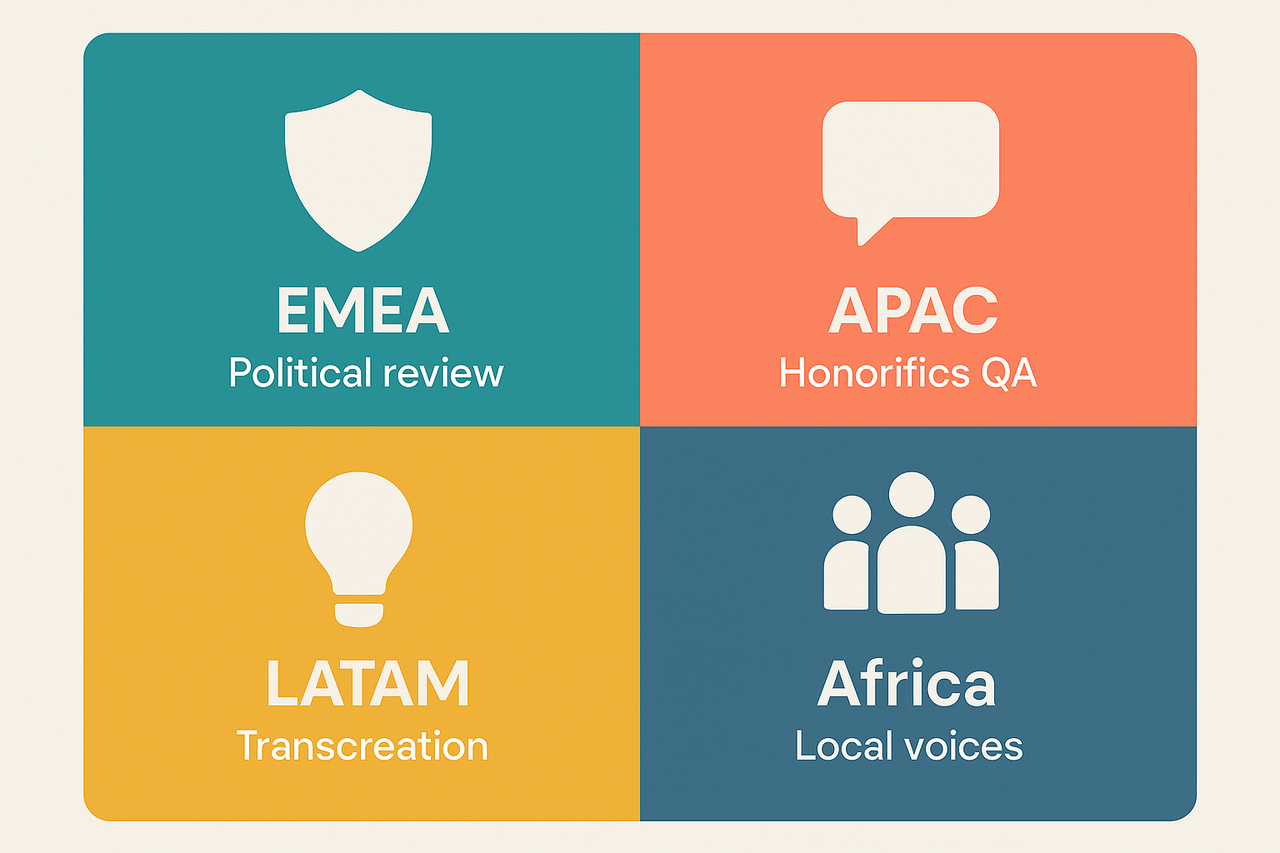
Real-world mini case studies (4 regions)
EMEA: Political and Brand Sensitivity
-
Detection: Social media monitoring and partner feedback flagged the issue.
-
Fixes: Removed dubbed segment, implemented political risk review, restricted edits to synthetic voices mimicking public figures, and updated prompt templates.
-
Quote: “We now tag scripts for political risk before any AI pass,” – Ana, Localization Lead
-
Mini-audit worksheet:
-
Notify: PR, legal, regional lead
-
Red-flag checklist: political figures, slogans
-
Review: regional counsel + PR sign-off
-
Monitor: 72 hours post-release
-
APAC: Dialects and Honorifics
-
Detection: Learner feedback and low course engagement.
-
Fixes: Created locale-specific style guides and prompt templates with honorifics, formal/casual variants, and native speaker QA.
-
Quote: “A single prompt tweak saved us weeks of rework,” – Kenji, L10n Manager
-
Mini-audit worksheet:
-
Register Matrix: Formal/Neutral/Casual by locale
-
Need for dialect variants: Yes/No
-
QA: Two native reviewers/locale
-
Voice asset rules
-
LATAM: Idioms and Register
-
Detection: Poor A/B results, social feedback
-
Fixes: Switched to transcreation workflows, idiom substitution with culturally appropriate equivalents, local copywriter involvement
-
Quote: “Transcreation beats literal translation every time,” – María, Creative Localization Lead
-
Mini-audit worksheet:
-
Idiom tagging
-
Transcreation owner
-
Glossary: approved phrases
-
Local reviewer sign-off
-
Africa: Minority Language Inclusion
-
Detection: Engagement data and NGO reporting
-
Fixes: Community partnerships, low-resource voice cloning, consent protocols, funded inclusivity efforts
-
Quote: “Coverage is a fairness metric for us now,” – Amina, Regional Content Lead
-
Mini-audit worksheet:
-
Language access chart
-
Priority coverage: population vs need
-
Consent checklist
-
Human-AI hybrid triggers
-
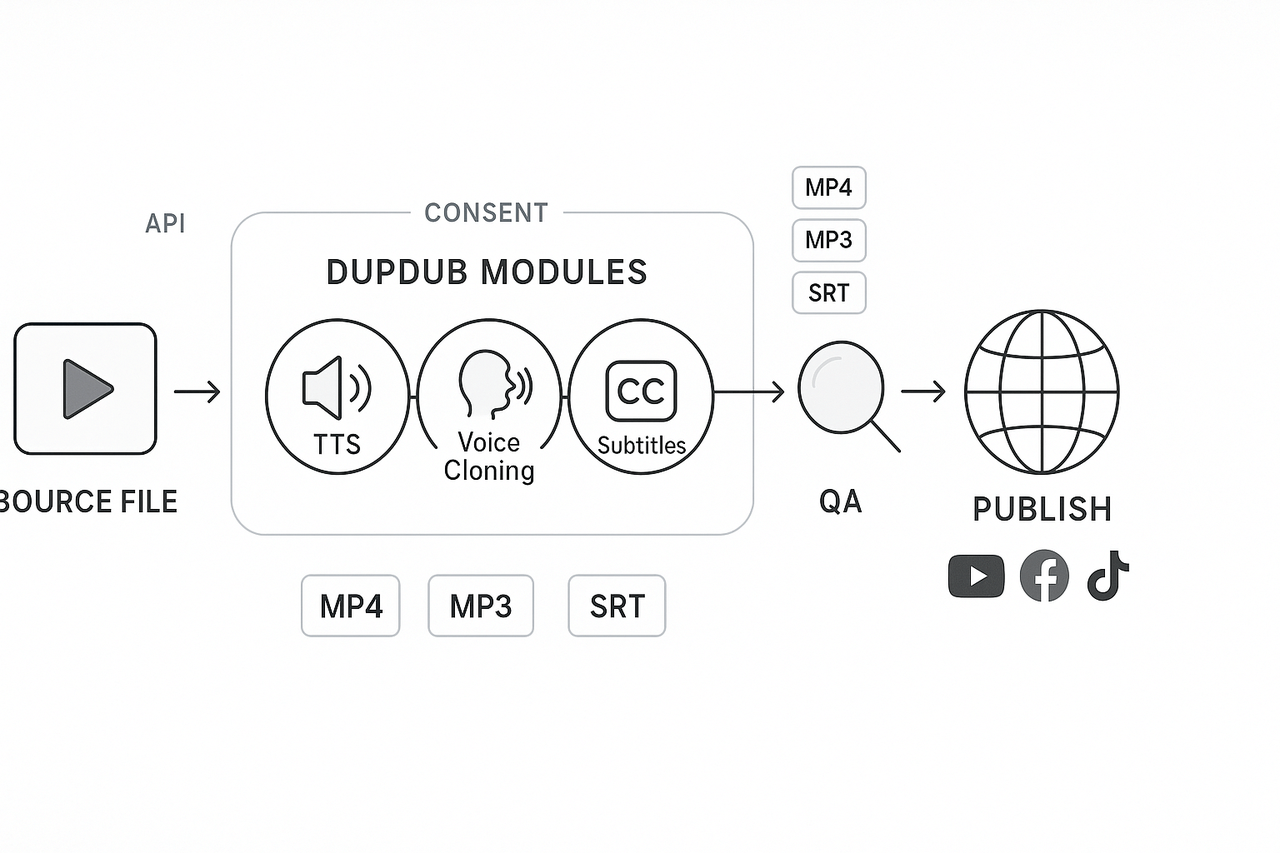
Tools, workflows and how DupDub fits
End-to-end workflow: source to publish
-
Source intake and prep Tools: DAM (digital asset management), project tracker, style guides. Collect scripts, raw video, and rights. Note language and cultural notes for target markets.
-
Transcription and source QA Tools: STT (speech-to-text) for fast transcripts, manual review. STT helps spot script changes and cultural flags early.
-
Translation and cultural adaptation Tools: CAT (computer-assisted translation), glossary manager, human linguists. Use a cultural adaptation checklist to flag tone, idioms, and visual references.
-
Voice selection and cloning in DupDub Tools: DupDub for voice cloning and TTS (text-to-speech). Create or choose a brand-aligned voice clone, or select a TTS voice that matches regional prosody.
-
Auto-alignment and timing Tools: DupDub subtitle alignment and waveform sync. Auto-align subtitles for accurate lip-sync and timing checks.
-
QA pass: linguistic and cultural review Tools: Native reviewers, style-check scripts, waveform thumbnails for timing, side-by-side audio/video comparisons.
-
Final polish and SFX Tools: DupDub AI sound effects, audio leveling, and simple editors for fades.
-
Publish and monitor Tools: CMS, social platforms, analytics. Tag content for ongoing monitoring and feedback loops.
DupDub features are mapped to the checklist
-
TTS and voice cloning: Choose from 700+ voices across 90+ languages. Maintain tonal consistency with brand-locked voice models.
-
STT (speech-to-text): Simplifies transcription and post-dub QA with accurate timestamping.
-
Auto-subtitle alignment: Enhances timing accuracy to match speaker lip movements.
-
API and automation: Enables bulk processing, approval workflows, and metadata logging for audit purposes.
-
Privacy safeguards: Systems for consent logging and voice cloning locks ensure ethical usage.
Governance, KPIs and Monitoring for Ethical Compliance
Assigning Ownership and Review Cadence
-
Policy Owner: Senior program manager responsible for ethical standards.
-
Technical Owner: Engineering lead focused on tool infrastructure.
-
QA Owner: Localization quality lead handling cultural accuracy.
-
Legal/Privacy Reviewer: Ensures compliance with regulations.
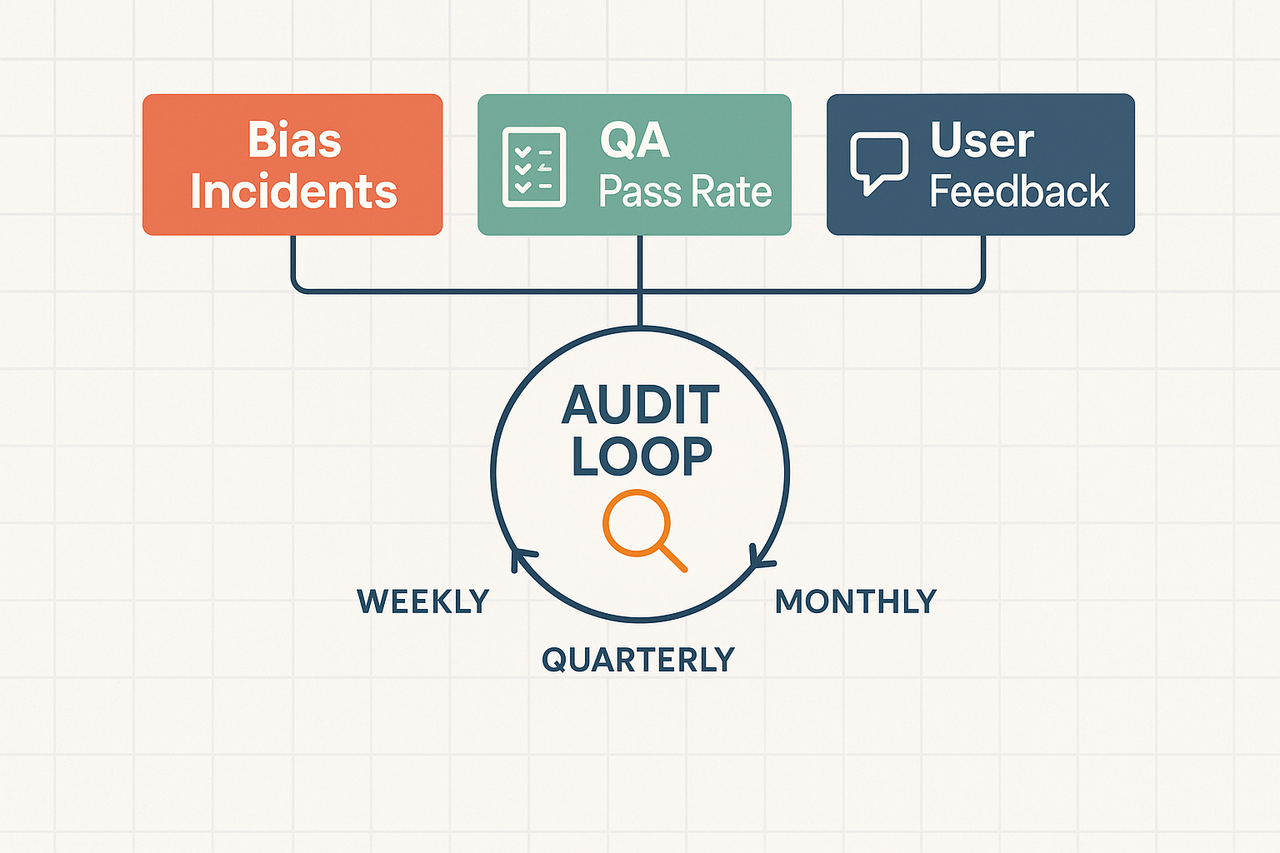
Defining Key KPIs for Ethical Oversight
-
Bias Incidents: Number and severity (tracked monthly).
-
QA Pass Rate: Percentage of content passing localized cultural and accessibility quality checks.
-
User Feedback Score: Average score from user ratings on a 1–5 scale.
-
Remediation Time: Days taken to resolve and publish fixes.
-
Consent Coverage: Percentage of content with verified voice/data consent.
Implementing Sampling and Audits
Monitoring with Tooling and Alerts
-
Accent, profanity, and sync mismatch detection tools.
-
Real-time flag reporting by users.
-
Change logs for subtitles and voiceover scripts.
Response and Remediation Workflow
Adhering to Regional Ethics & Policy
Dashboard Visualization
-
Top row: Bias Incidents, QA Pass Rate, User Feedback (color-coded blocks).
-
Middle section: trend graphs over time.
-
Bottom area: sample audit outcomes and current incident log.
-
Sidebar filters by region, language, and media type.
Balancing automation with human oversight and workforce impact
Keep humans in these stages
-
Creative transcreation and tone decisions
-
Final voice sign-off and fidelity checks
-
Sensitive topics, legal or political content reviews
-
Any customer-facing voice cloning deployments
Reskilling, contractor rights, and consent
-
Offer certification and hours for tool proficiency
-
Standardize voice licensing clauses for contractors
-
Store consent records and versioned usage rights
-
Pay for voice reuse, audits, and attribution
Implementation checklist
Week-by-week rollout plan
- Week 1: Project setup and scope. Define target markets, key stakeholders, and success metrics. Collect source assets and brand voice notes. Secure any voice consent forms.
- Week 2: Pilot content and policy draft. Localize 1 short pilot video per region. Draft the ethics code and review with legal and local reviewers.
- Week 3: Human review and iteration. Run linguistic QA, verify cultural adaptation, and update the style guide and glossary.
- Week 4: Scale and automation. Add DupDub API or batch workflows, set monitoring KPIs, and train reviewers on tooling.
- Week 5: Governance and reporting. Publish the code, set audit cadence, and assign escalation owners.
- Week 6: Measure and iterate. Review KPIs, collect viewer feedback, and update templates.
Printer-friendly pre-publish QA checklist
- Confirm transcript accuracy and timecodes.
- Verify translated copy matches intent, not literal words.
- Check voice choice for age, gender, and regional fit.
- Ensure consent is recorded for any voice clone.
- Validate on-screen text, graphics, and cultural references.
- Run audio loudness and sync checks.
- Save master files and export SRT and MP4 for stakeholders.
Sample policy language (snippets to adapt)
- "We require documented consent for voice cloning and store consent records with the asset."
- "All localized audio must pass a regional cultural review before publication."
- "Sensitive topics get an elevated review by local subject experts."
Contact and escalation template
- Primary owner: Name, role, email, phone.
- Regional reviewer: Name, role, SLA for response (e.g., 24 hours).
- Escalation: If unresolved in 48 hours, notify Legal and Product leads.
How to run the DupDub ethical localization demo (3-day free trial)
- Sign up for the free trial and pick one short source video (60 to 120 seconds).
- Upload the file, auto-transcribe, and attach your source transcript and brand notes.
- Choose target locales and either a cloned voice (with consent) or a matching TTS.
- Generate side-by-side outputs, export MP4 and SRT, and run the mini-audit worksheet.
- Share deliverables with reviewers and collect feedback using the included QA checklist.
FAQ — People Also Ask & common concerns
-
Can we clone voices ethically for dubbing?
Yes, in many contexts. Require explicit informed consent from the speaker and limit reuse cases. Document permissions, allowed languages, and retention in your AI localization ethics code. Audit voice provenance and enable easy revocation.
-
How do we measure cultural accuracy in localization and cultural adaptation?
Use a mix of native reviewer scores, qualitative feedback, and quantitative metrics. Track comprehension, tone match, and engagement by the audience. Do A/B tests and community reviews, and score deliverables with an audit worksheet.
-
Do we need consent for voice cloning and who must sign off?
Yes. Get recorded, written consent covering cloning, languages, and redistribution. Legal, IP, and a localization lead should approve, and store consent records with access logs. See the Implementation checklist and AI dubbing cluster pages for templates and demos.

