-
Cost savings: replacing studio dubbing often lowers direct spend per minute by several dozen to a few hundred dollars, depending on voice fees, studio time, and revisions.
-
Speed gains: AI workflows let teams publish translated videos in days, not weeks, because automated alignment and instant TTS remove scheduling bottlenecks.
-
Quick test: model your own numbers in the interactive calculator later in this guide to see the exact ROI for your content mix.

Why localization ROI matters for SMBs and creators
Why it pays off
Budget mistakes that erode ROI
-
Skipping quality checks: poor voice or sync kills engagement, wasting the initial spend.
-
Treating localization as one-off: copy and assets often need updates, so costs recur.
-
Ignoring platform optimization: subtitles, thumbnails, and metadata carry incremental returns.
-
Over-relying on expensive studios for low-value content: not every asset needs premium studio dubbing.
-
No performance tracking: if you don’t measure, you can’t prove ROI or optimize spend.
Recurring versus one-time costs, and cash flow impact
Core production costs
-
Transcription and translation: Transcription charges per minute convert speech to text. Translation is often per word or per minute. These recur for each new asset or update.
-
Studio dubbing (traditional): Studio rates include voice talent, studio time, director, and post-production. Expect per-minute or per-hour billing and setup fees for each language.
-
AI dubbing and voice cloning: Platform fees, credits or pay-as-you-go costs, and occasional voice clone setup. These are typically lower per minute and scale with volume.
Quality and localization QA
-
LQA, or language quality assurance, checks style, tone, and lip sync in video. LQA is often priced per minute or per hour and recurs every time you localize new content.
-
Subtitling and captioning: Auto-generated captions cut costs, but human cleanup is a recurring cost for accuracy and accessibility.
Platform, engineering, and integration
-
CMS and API integration: One-time engineering work to connect localization tools to your workflow. Budget for project hours and a small post-launch bug window.
-
Encoding, hosting, and delivery: Video processing and CDN fees can be recurring if you host localized versions separately.
Ongoing maintenance and governance
-
Content updates: Re-dubbing or re-translating edits adds variable, recurring costs.
-
Voice library management: Maintaining cloned voices or brand voice guides costs time or platform credits.
-
Reporting and analytics: Tools and analyst time to measure performance and ROI.
Hidden costs and compliance
-
Legal review: Contracts, rights clearances, and talent releases may add one-time or per-language fees. This is often overlooked.
-
Accessibility work: Extra time for audio descriptions or expanded captions is recurring per project.
-
Regional distribution costs: Platform fees or retailer formatting can appear late in the project.
Quick budgeting examples
-
Small creator monthly pipeline: 10 videos, short edits: budget the recurring costs for transcription, AI dubbing credits, light LQA, and captions. One-time costs: voice clone setup and integration.
-
SMB product course launch: single big project: expect high upfront studio or engineering fees, followed by lower per-module translation costs.
Typical studio workflow and per-minute examples
|
Use case
|
Studio (per finished minute)
|
AI dubbing (per finished minute)
|
Time-to-publish
|
|
Short marketing video
|
$300$600
|
$10$50
|
Studio 2–5 days, AI same day to 48 hours
|
|
E-learning module
|
$700$1,200
|
$30$100
|
Studio 5–10 days, AI 24–72 hours
|
AI dubbing pipeline and where time is saved
Quality tradeoffs and practical hybrid workflows
-
Generate AI dubs and auto-sync subtitles.
-
Run in-house LQA for brand tone, legal checks, and timing.
-
Tweak the voice model or re-record key lines with voice talent.
-
Only send final, high-value assets to the studio when needed.
How we built the DupDub Cost Calculator: methodology + ROI formula
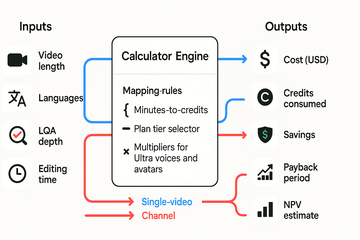
Calculator inputs: what you type in
-
Video length in minutes. This drives base minutes for TTS or re-voicing.
-
Number of target languages. Multiplies minutes and LQA checks.
-
LQA depth (light, standard, strict). This adjusts human review minutes per language.
-
Post-editing time per language (minutes), for syncing and fixes.
-
Voice cloning or custom voices (yes/no), which adds a one-time setup cost.
-
Turnaround preference (standard vs rush), which adjusts cost multipliers.
How credits and plans map to cost
ROI formulas we use
-
Savings per video = Studio dubbing cost per language minus DupDub cost per language.
-
Total project savings = Savings per video × number of target languages.
-
Payback period (months) = Upfront DupDub investment / Monthly savings. Use this if you buy a monthly plan or credits up front.
-
Basic NPV-style estimate: NPV = Σ (Net savings_t / (1 + r)^t) for t = 1..T. The calculator defaults to r = 8% (annual) and T = 12 months for short libraries. It sums monthly savings, applies the discount, and returns a simple NPV number.
Why credits match real-world minutes, and quick wins
-
Single-video bursts: Great for testing. You’ll see immediate per-video savings and a short payback if you only need a few languages.
-
Channel or library models: Batch localization spreads the cost of voice cloning and monthly plans across many videos, shrinking per-video cost and increasing ROI over time.
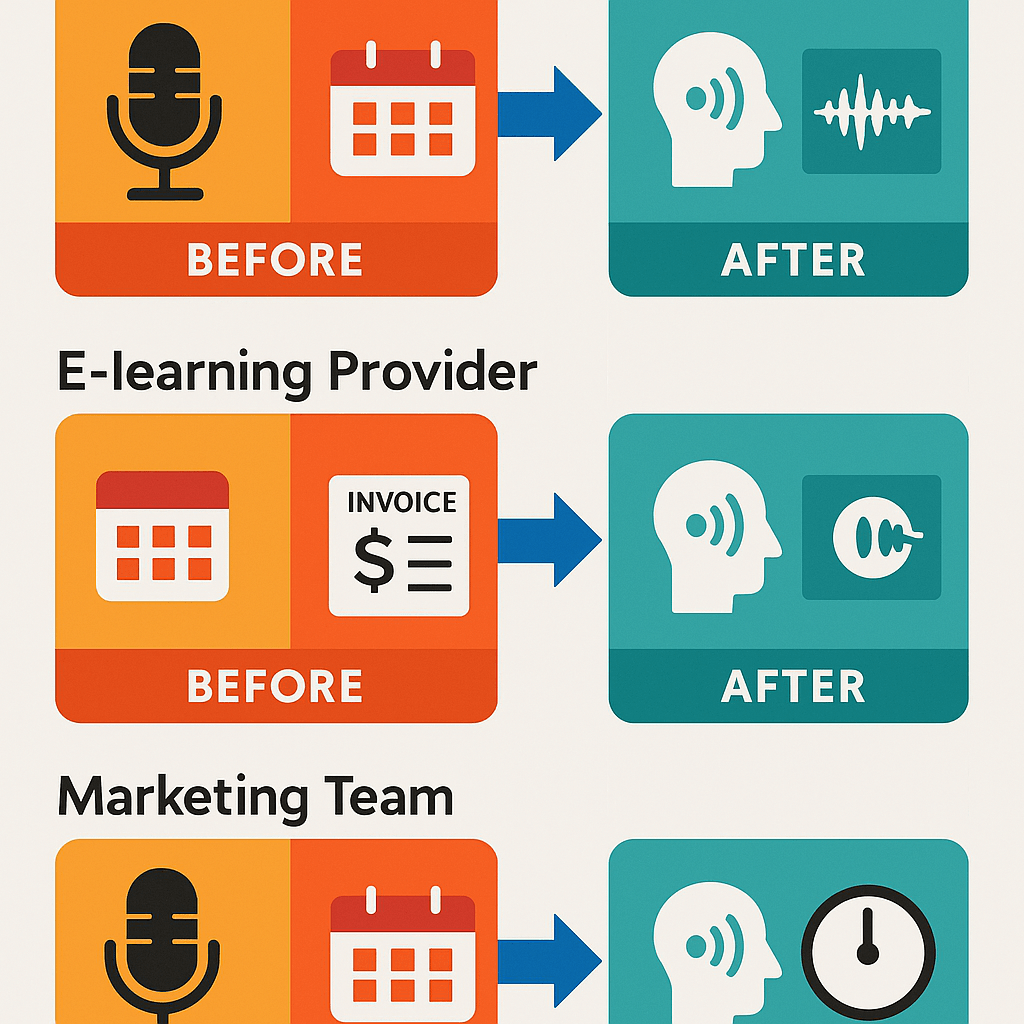
Real SMB mini case studies and example budgets
YouTuber: grow audience by dubbing three languages
|
Metric
|
Before (studio)
|
After (AI dubbing)
|
|
Languages
|
3
|
3
|
|
Voice actors + studio time
|
$1,200
|
$0 (AI voice clone)
|
|
Editing & mixing
|
$200
|
$30
|
|
Subtitles & alignment
|
$100
|
$10
|
|
Turnaround
|
14 days
|
24 hours
|
|
Total
|
$1,500
|
$$40$$100 (credits)
|
-
Audio minutes: 10, languages: 3, voice cloning: yes.
-
Revisions: low to medium, factor 1–2 editing hours per video.
-
Delivery SLA: tight timeline reduces opportunity costs.
E-learning provider: consistent voice, faster courses
|
Metric
|
Before (studio)
|
After (AI workflow)
|
|
Modules
|
50 x 5 min
|
50 x 5 min
|
|
Casting + recording
|
$12,000
|
$0 (single clone)
|
|
Post production
|
$3,000
|
$500
|
|
Turnaround
|
30 days
|
5 days
|
|
Total
|
$15,000
|
$$500$$1,200
|
-
Total audio minutes: 250, cloning required.
-
Include LQA (linguistic QA) and caption costs.
-
Use bulk pricing where applicable.
Marketing team: ad campaign across five markets
|
Metric
|
Before (studio vendors)
|
After (AI dubbing)
|
|
Markets
|
5
|
5
|
|
Voice talent + fees
|
$10,000
|
$0 (TTS + cloned voice)
|
|
Subtitles & variants
|
$1,000
|
$150
|
|
Turnaround
|
6 weeks
|
7 days
|
|
Total
|
$11,000
|
$$300$$800
|
-
Markets: 5, ad minutes per country input.
-
Add brand review and legal approval time.
-
Factor in opportunity gain from time-to-market boost.
Hidden costs, risks, and how to mitigate them
Quality control and LQA checkpoints
-
Verify subtitle timing and speaker turns.
-
Confirm translated copy matches intent, not literal words.
-
Spot-check voice clone accuracy for prosody and emotion.
-
Run a final audio/video sync pass.
Accessibility and compliance
Platform fees, limits, and contractual risk
-
Ask for SOC or security summaries and data retention policies.
-
Verify voice-clone consent and usage locks.
-
Include SLAs for uptime and quality remediation.
-
Add indemnity language for IP and privacy breaches.
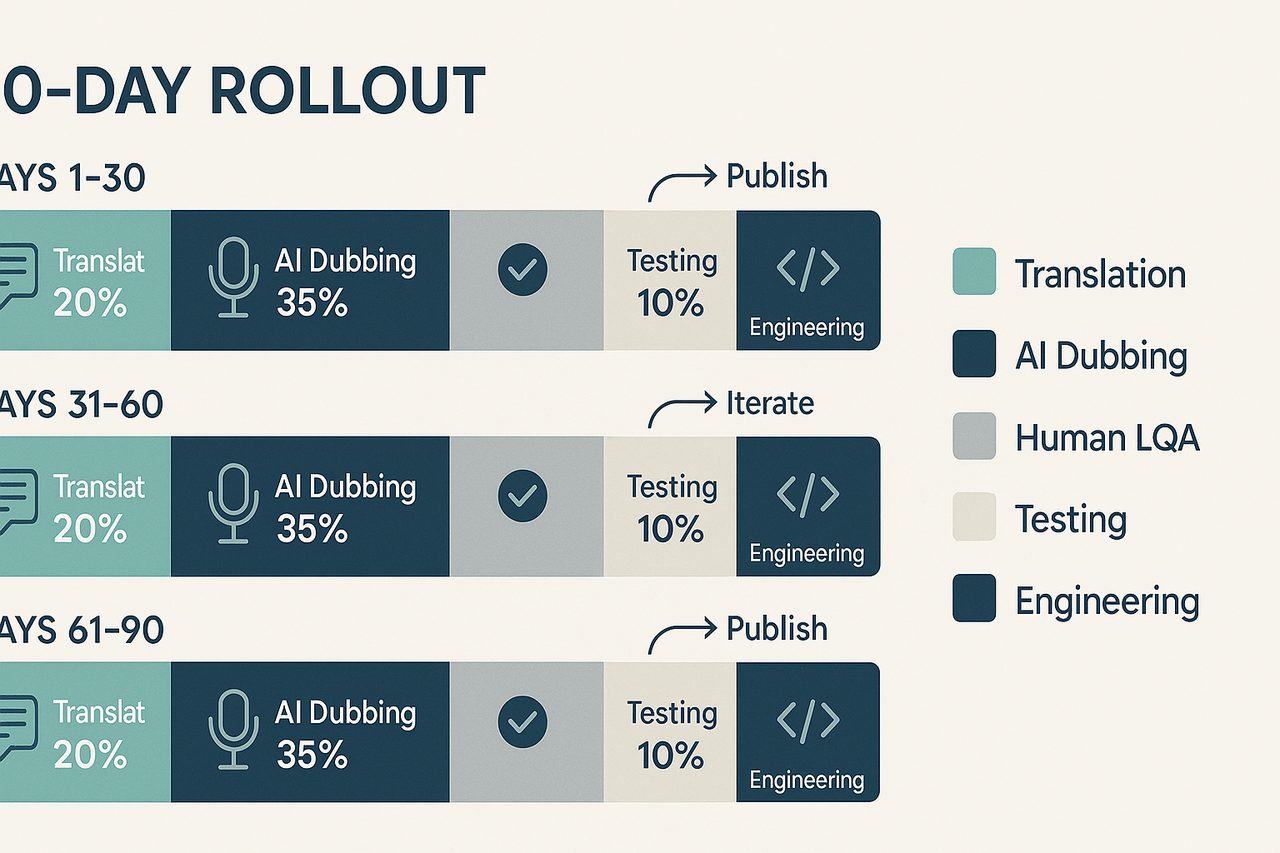
Build your localization budget: a step-by-step checklist and timeline
90-day checklist: fast wins first
-
Content audit: tag videos by views, revenue, and evergreen value. Prioritize the top 20 percent that drives most engagement.
-
Market pick: choose 2 to 4 priority markets using audience data. Match language with top social platforms.
-
Voice & tone: pick 1 brand voice per market and test one clone or TTS style.
-
Script prep: export transcripts, trim filler, and create localized copy for subtitles.
-
LQA gates: set light quality checks at 1st draft and pre-publish. Define pass/fail criteria.
-
Mix plan: decide the AI/human split by content type and risk. Use AI dubbing for low-risk content.
-
Tech & integrations: map export formats, CMS uploads, and YouTube/learning platform steps.
-
Measurement: define KPIs, rollout cadence, and revenue attribution rules.
Sample 90-day rollout timeline
Allocate your first-year budget
FAQ — common questions about localization budgets and AI dubbing
-
Per-minute AI dubbing cost: what to expect for your localization budget
AI dubbing prices vary by voice quality, language, and platform. Expect a low-end TTS voice to cost under $5 per finished minute, advanced cloned voices to land in the $10 to $60 per finished minute range, and full studio dubbing to run $200 to $1,000 plus per minute.
-
When should voice cloning replace human actors for dubbing projects
Use voice cloning when you need scale, fast turnaround, or a consistent brand voice across markets. Keep human actors for high-emotion scenes, union projects, or when local nuance matters. Pilot clones on a small sample and include linguistic quality assurance (LQA) checks before full rollout.
-
How to measure localization ROI and justify a bigger localization budget
Measure ROI as (Incremental revenue minus localization cost) divided by localization cost. Track leading indicators: views by region, click-through rate, conversion lift, and retention. Use A/B tests, the DupDub cost model, and the downloadable budget spreadsheet to forecast payback period in months.
-
Is voice cloning safe: data privacy and security for enterprise voice cloning
Check consent, encryption, and retention policies before you clone a voice. Prefer vendors that lock clones to the original speaker and offer secure processing and deletion options. Add contract clauses for data handling and run a legal review for sensitive markets.
-
Where to test audio and video quality before you commit your localization budget
Do a small pilot with 1 to 3 minutes of core content, and run A/B tests against the original. Use LQA reviewers native to the target language, and test on real devices and platforms. Try a free trial or demo path to audition voices and export samples before scaling.

