-
Speed: a single episode can be localized in hours, not days.
-
Cost: automated workflows cut studio and talent fees.
-
Quality: good results come from testing voices and tightening subtitle timing.
-
Scale: reuse scripts, subtitles, and cloned voices across a series.

Why podcast dubbing matters now: reach, retention and revenue
Reach: tap non-English markets faster
Retention and monetization improve with native audio
When to dub, subtitle, or translate notes
-
Dub the episode when you want full engagement and brand voice preserved across markets. Go audio-first for narrative shows, interviews, and ad reads.
-
Use subtitles only for video clips or social promotion, where quick skims work.
-
Translate show notes when budget or speed matters, or to improve SEO without full localization.
-
Mix approaches for experiments: dub flagship shows, subtitles for clips, translated notes for long-tail SEO.
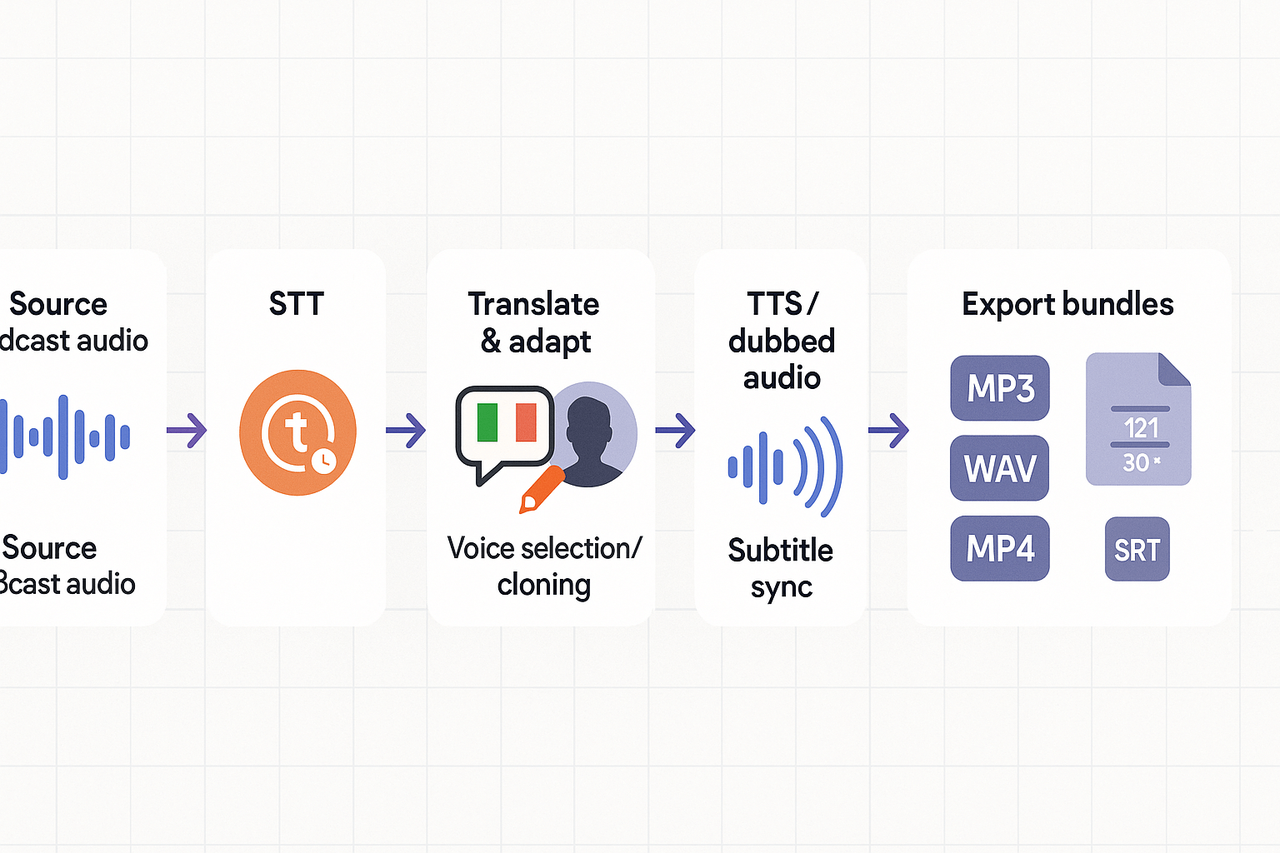
How AI dubbing and audio localization work (simple technical primer)
Core pipeline: step-by-step
-
Speech-to-text (STT): Convert the source audio into time-stamped transcripts. Good STT captures punctuation, speaker turns, and timestamps for each phrase.
-
Translate and adapt: Translate text into target languages, then adapt idioms, cultural references, and pacing so the result reads naturally.
-
Voice selection or cloning: Pick a synthetic voice or create a voice clone from a short sample. Cloning preserves a host’s timbre across languages.
-
TTS or dubbed render: Use TTS (text-to-speech) or the cloned voice to generate audio, matching phrasing and emotion.
-
Subtitle sync and captions: Align translated text with original timecodes for on-screen captions and transcripts.
-
Final mastering: Equalize, normalize loudness, add ambient SFX if needed, and export audio and subtitle files.
Voice cloning vs TTS
-
Voice cloning creates a personalized voice from a short sample. It’s great for brand continuity. It needs consent and careful quality checks.
-
TTS offers more voices and quicker iteration. It’s lower risk and faster to scale across many languages.
Quality checkpoints and trade-offs
-
Initial STT accuracy, then review translated script for cultural fit.
-
Pronunciation and prosody checks after the first TTS pass.
-
Subtitle timing review against speech to meet accessibility.
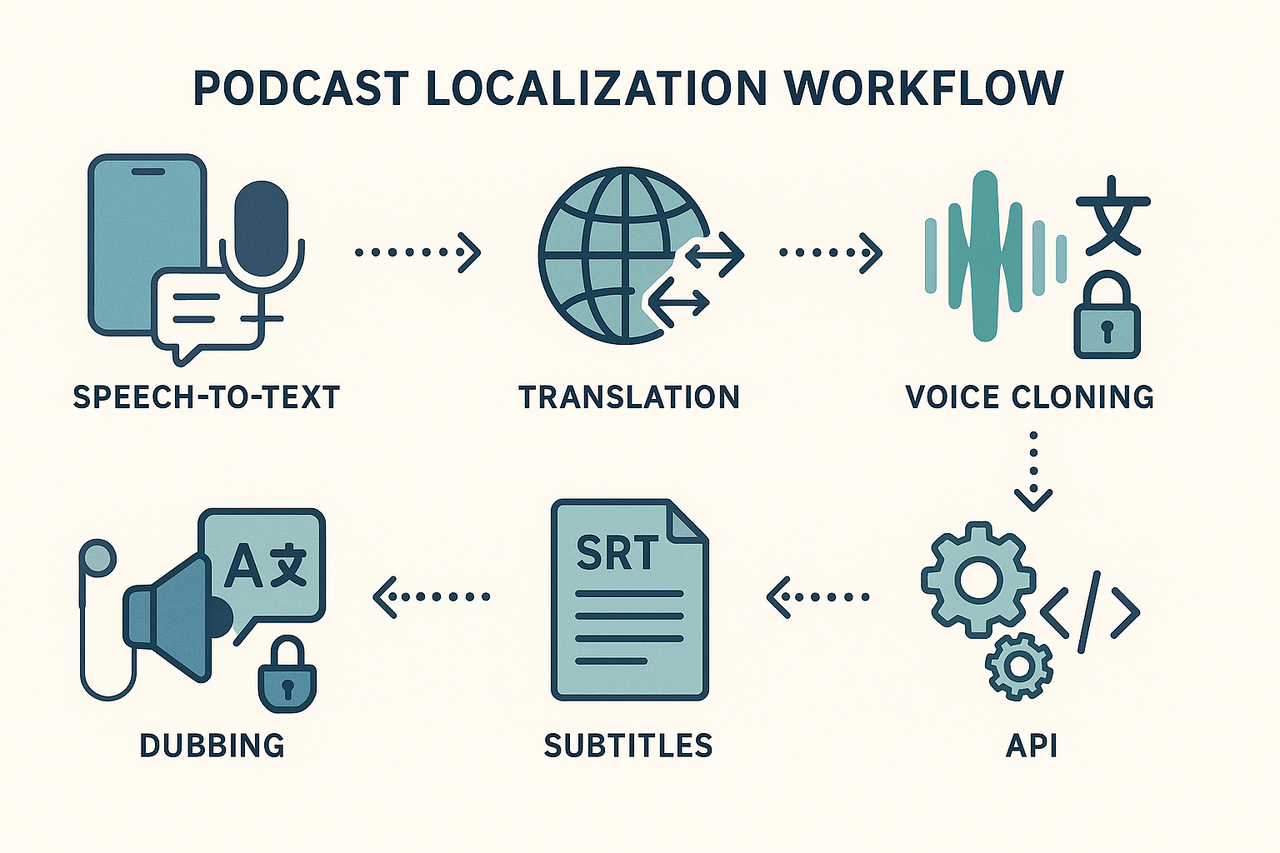
DupDub for podcast multilingualization: features, pricing & demo assets
Core features podcasters need
-
Speech-to-text (STT): Fast, multilanguage transcription to create an editable script.
-
Machine translation: Translates episode scripts while keeping timing and meaning.
-
Voice cloning: Creates a synthetic version of a host voice from a short sample.
-
AI dubbing and alignment: Auto-syncs translated audio to original timestamps.
-
Auto-subtitles and SRT export: Generates, translates, and exports subtitle files.
-
Browser recording and editing studio: Record, edit, and preview dubbed takes in one place.
-
API and integrations: Automate batch dubbing and connect to CMS or publishing tools.
-
Export formats: MP3, WAV for audio; MP4 and SRT for packaged episodes.
Pricing and trial overview
Demo audio, screenshots and test assets
Security, privacy, and enterprise controls
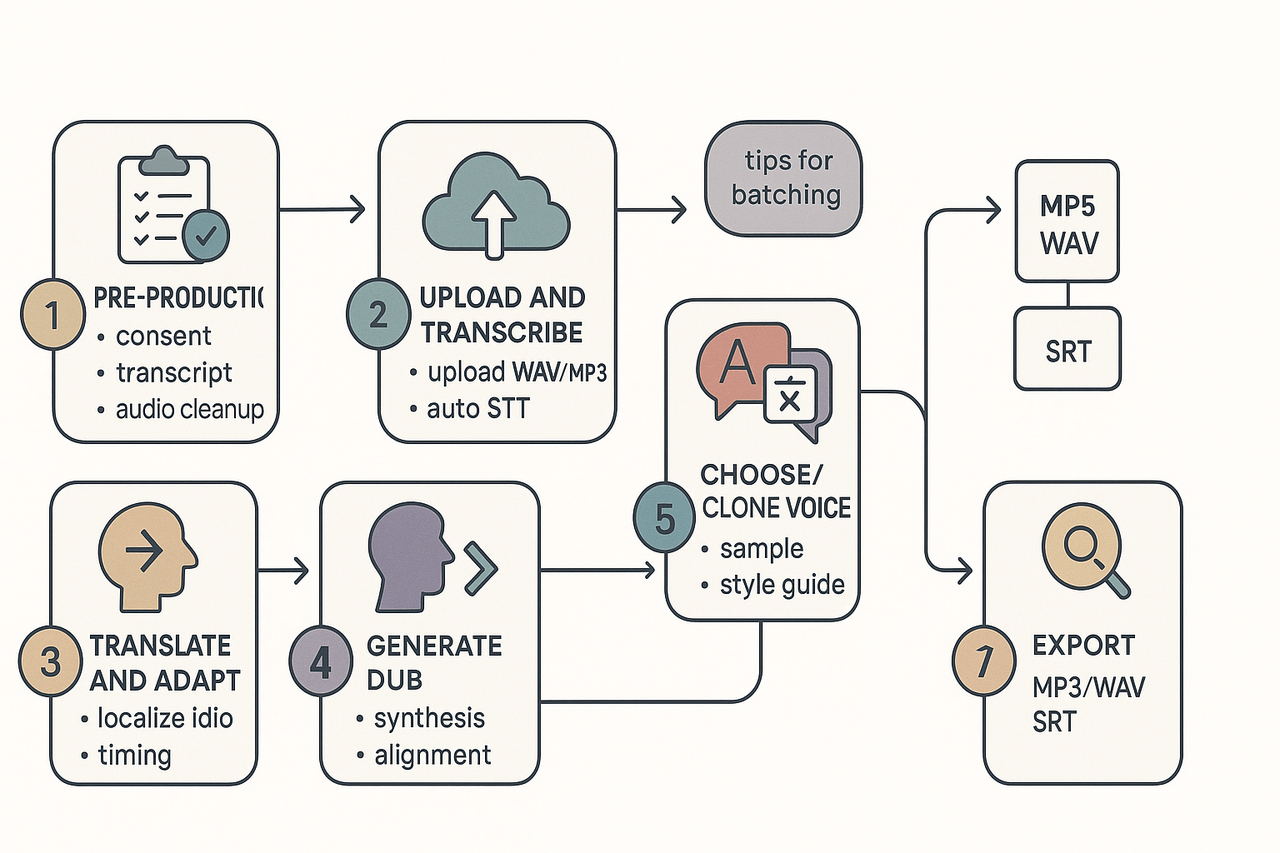
Step-by-step: How to dub a podcast episode with DupDub (practical tutorial)
Before you start: pre-production checklist
-
Get consent and rights. Confirm guest approvals and any music licensing before translating or cloning voices.
-
Create a clean transcript. Use your native editor or export a platform transcript. Clean speaker labels and filler words first.
-
Fix audio quality. Apply noise reduction, normalize levels, and remove clipping. Good source audio reduces artifacts in the dub.
-
Set language and tone. Decide target languages and style notes: formal vs conversational, regional accents, culturally relevant references.
Upload and automatic transcription
-
Export your final, cleaned file as WAV or high-bitrate MP3.
-
Upload to the studio and run automatic speech-to-text (STT). Edit the transcript for accuracy and speaker turns.
-
Create chapter markers or timestamps for key segments, ads, and sponsor reads. These make alignment simpler.
Translate and adapt the script
-
Auto-translate the transcript, then manually adapt idioms and local references. Machine translation is a draft, not a final script.
-
Shorten long sentences so the translation matches original timing when possible. Keep natural phrasing for flow.
-
Mark timing-critical lines, like branded calls-to-action, for manual attention during alignment.
Choose or clone voices: best practices
-
Pick a voice with a matching energy and pacing to the host. Test 30-second samples first.
-
For voice cloning, supply a clean 30 to 60 second sample and a short style guide. The platform locks clones to the original speaker for security.
-
Use separate voices for ads, narration, and hosts to preserve clarity.
Generate, QA, and export
-
Generate the dub and review by segment. Check timing, intonation, and any mistranslations.
-
Run a QA pass: loudness, breath sounds, sync, and subtitle timing. Use an internal checklist for repeatability.
-
Export final files: MP3 or WAV for audio, and SRT for subtitles. For series batching, automate transcript upload and voice assignment in bulk.
Voice selection, quality tuning and localization best practices
Pick the right voice
Tune prosody and quality
Handle idioms and cultural phrasing
QA checklist and audio mastering tips
-
Native listener pass: check tone, idiom handling, and offense risk.
-
Timing check: ensure subtitle and audio sync within 200 ms where possible.
-
Loudness: normalize to -16 LUFS for stereo podcasts and -19 LUFS for mono, then true-peak limit to -1 dBTP.
-
EQ and leveling: cut low rumble, gentle 2-4 dB boost around 2-4 kHz for clarity, compress lightly for consistent loudness.
-
Final listen: compare original and dubbed tracks back to back.
Real podcaster case studies & mini-interviews (results you can expect)
Indie interview show: expanded reach in three markets
Educational podcast: cut localization cost and turnaround
Small series: scale with batch dubbing and consistent voice
-
Expect downloads to grow where language barriers existed.
-
Plan for 50–70 percent cost savings versus traditional dubbing.
-
Build a batch workflow to scale episodes without extra staff.
Legal, ethical and accessibility considerations for dubbing podcasts
Consent and Usage Rights
-
Always obtain written or recorded consent from podcast hosts and guests prior to using or cloning their voices.
-
Clearly define allowed uses, including which languages the dubbing may appear in, distribution channels, usage duration, and commercial uses.
-
Maintain detailed rights management records for every episode.
-
Allow contributors to revoke consent and reflect these changes in your systems.
Ethical Use of Voice Cloning
-
Use synthetic voices only when explicit permission has been given.
-
Communicate how voice data will be stored, used, and deleted.
-
Restrict use to agreed-upon contexts and include human review for sensitive material.
-
Inform listeners using visible or audible disclosures where synthetic voices are used.
Accessibility and Legal Compliance
-
Provide transcripts and captions for every dubbed episode.
-
Follow standards such as WCAG 2.1 to make sure content is usable by people with disabilities.
-
Supply downloadable SRT (subtitle) files and confirm media players support screen readers and keyboard navigation.
Decision matrix snapshot
|
Vendor
|
Languages (scope)
|
Cloning fidelity
|
Integrations
|
Pricing model
|
Enterprise features
|
|
DupDub
|
90+ TTS, 47 cloning
|
High, multilingual clones
|
Browser studio, API, Canva plug-ins
|
Free trial, subscriptions, credits
|
Voice lock, encrypted processing, team controls
|
|
ElevenLabs
|
50+
|
Very high naturalness, clone tweaks
|
API, studio
|
Subscription, pay-as-you-go
|
Fine-grain voice access, priority support
|
|
Murf AI
|
30+
|
Good for narration
|
Studio, plugin integrations
|
Subscription
|
Branding controls, team accounts
|
|
Speechify
|
20+
|
TTS-focused, limited cloning
|
Apps, browser
|
Subscription
|
Accessibility-first tooling
|
|
Others (Play.ht, HeyGen, Synthesia)
|
Varies
|
Varies by use case
|
Varies
|
Mixed models
|
Media-centric enterprise options
|
How to run fair trials and what to measure
-
Use the same episode clip across vendors, 60 to 90 seconds long.
-
Test identical target language and one voice clone per vendor.
-
Measure: listener comprehension, naturalness (1–5), timing drift, and time to publish.
-
Track cost per minute and minutes of usable output.
-
Run A/B listens with real listeners for retention lift.
Technical checks for voice quality and subtitle alignment
-
Check prosody and emotion match the source.
-
Verify phoneme accuracy for names and jargon.
-
Confirm subtitle timing within 200 ms of speech.
-
Test loudness consistency and normalize peaks.
-
Inspect cloned voice artifacts around plosives and sibilants.
FAQ: common questions podcasters ask about dubbing and audio localization
-
How accurate is podcast dubbing AI? podcast dubbing accuracy expectations
Expect good results for clear speech, short sentences, and scripted segments. Accuracy drops on heavy accents, overlapping talk, slang, or poor audio. Always review the auto transcript and do a quick human edit before publishing.
-
Can you preserve a host's voice, preserve the host in dubbing
Yes, voice cloning can retain a host's tone across languages with a short recording sample. Quality varies, so test clones and get consent from the speaker before cloning.
-
What language coverage is typical for audio localization
Coverage ranges by tool, from 40 to 90+ languages for TTS and subtitles. Check the platform limits for cloned voices and STT languages; see DupDub docs for specific language support.
-
What are the main dubbing cost drivers, dubbing cost drivers and pricing
Common drivers: episode length, voice quality tier, cloning setup, number of target languages, and human editing time. Plan for credits or minutes plus post-editing labor.
-
What consent and legal steps should I take, and what are the best practices for podcast dubbing
Get written consent from hosts and guests for voice use and cloning. Store samples securely, log permissions, and disclose synthetic voices when required. Keep records for future audits.

