-
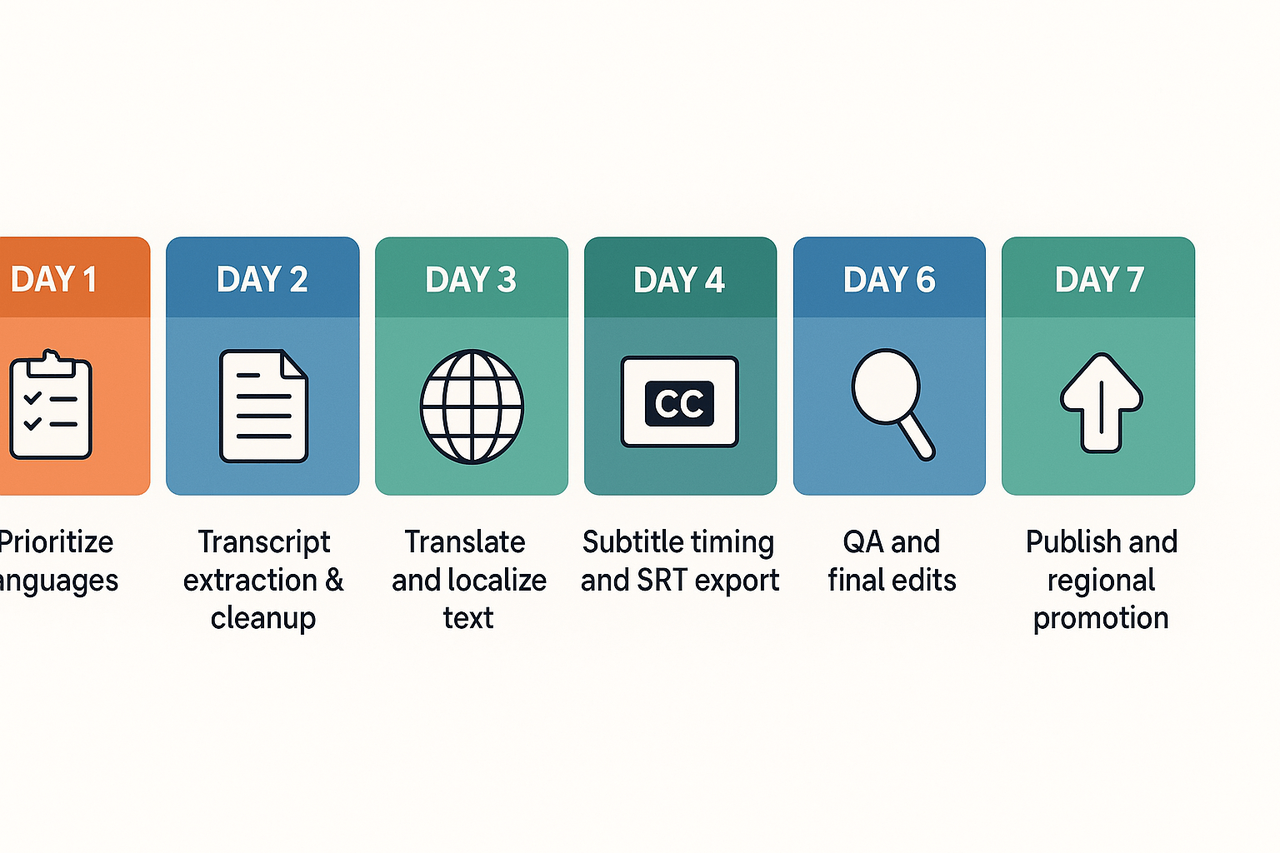
Day 1: Pick 2–3 priority languages based on current analytics and target growth.
-
Day 2: Extract clean transcript (auto captions plus manual fixes).
-
Day 3: Translate transcript and localize on-screen text and cultural notes.
-
Day 4: Create timing-adjusted subtitles and export SRTs.
-
Day 5: Produce dubbing or voiceovers and align audio to video.
-
Day 6: QA, tweak timing, and finalize edits (sound levels, captions).
-
Day 7: Publish localized versions with local titles, descriptions, and promote in regional channels.
Why YouTube Localization Matters (short, data-driven)
When localization moves the needle
-
High search demand outside your language, shown by international keyword volume.
-
Evergreen tutorials, how-to guides, and product explainers.
-
Top-performing shorts and long-form with steady watch time.
Which channel types gain the most
-
A spike in impressions from new countries after publishing translations.
-
Watch-time per viewer rising in localized versions.
-
Higher click-through rates on localized thumbnails and titles.
A Step-by-Step Video Localization Roadmap for YouTubers
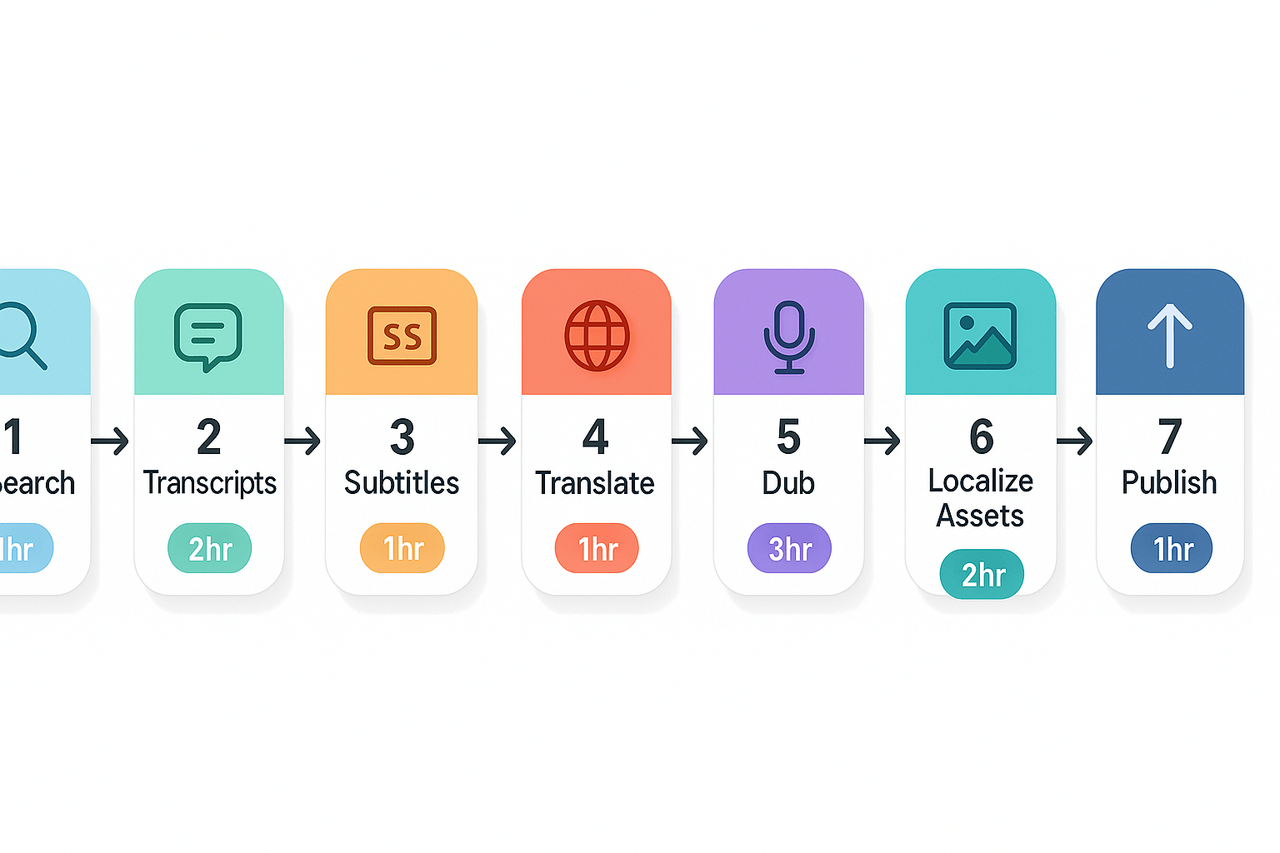
Step 1: Audience and market research
-
Tasks: check YouTube Analytics for top countries, run keyword searches in target languages, survey fans in comments or community posts.
-
Time: 2 to 6 hours per video series.
-
Quality checkpoint: chosen languages cover at least 60 percent of incremental global watch time.
Step 2: Create accurate transcripts (speech to text)
-
Tasks: export auto-captions, correct speaker labels, split long sentences for natural reading.
-
Tools: built-in YouTube captions or an automated speech-to-text tool with 40+ languages.
-
Time: 30 to 90 minutes per 10 minutes of video.
-
Quality checkpoint: transcripts match spoken audio with 95 percent accuracy.
Step 3: Generate and style subtitles
-
Tasks: set line length to 32 characters, keep two lines max, add speaker tags when needed.
-
Time: 15 to 45 minutes per language for a 10-minute video.
-
Quality checkpoint: no subtitle reads longer than 6 seconds and no overlap errors.
Step 4: Translate and localize the script
-
Tasks: machine translate then human edit, adapt jokes or references, produce a localized script for dubbing and on-screen text.
-
Time: 1 to 3 hours per language depending on review depth.
-
Quality checkpoint: a native reviewer confirms natural phrasing and tone.
Step 5: Produce dubs and voiceovers
-
Tasks: align localized script to timestamps, generate AI voiceovers or record actors, adjust timing and breathing.
-
Tools: platforms that handle text-to-speech, voice cloning, and subtitle alignment work fastest. (One tool in that category can run the full workflow end to end.)
-
Time: AI dub for a 10-minute video in 10 to 30 minutes; professional recording takes 2 to 8 hours.
-
Quality checkpoint: lip sync and pacing feel natural, and the localized voice matches channel tone.
Step 6: Localize on-screen assets and metadata
-
Tasks: create translated thumbnails, localize on-screen text, add localized chapters and translated descriptions.
-
Time: 1 to 4 hours per language.
-
Quality checkpoint: thumbnails and titles pass a native speaker A/B check for clarity and appeal.
Step 7: Publish, promote, and iterate
-
Tasks: publish translated versions or language-specific uploads, run targeted ads or community posts, gather viewer feedback.
-
Time: initial monitoring 7 to 14 days after release.
-
Quality checkpoint: measure watch time, CTR on localized thumbnails, and retention by country.
How DupDub Fits Into Each Step (workflow & demo)
Map features to each roadmap step
-
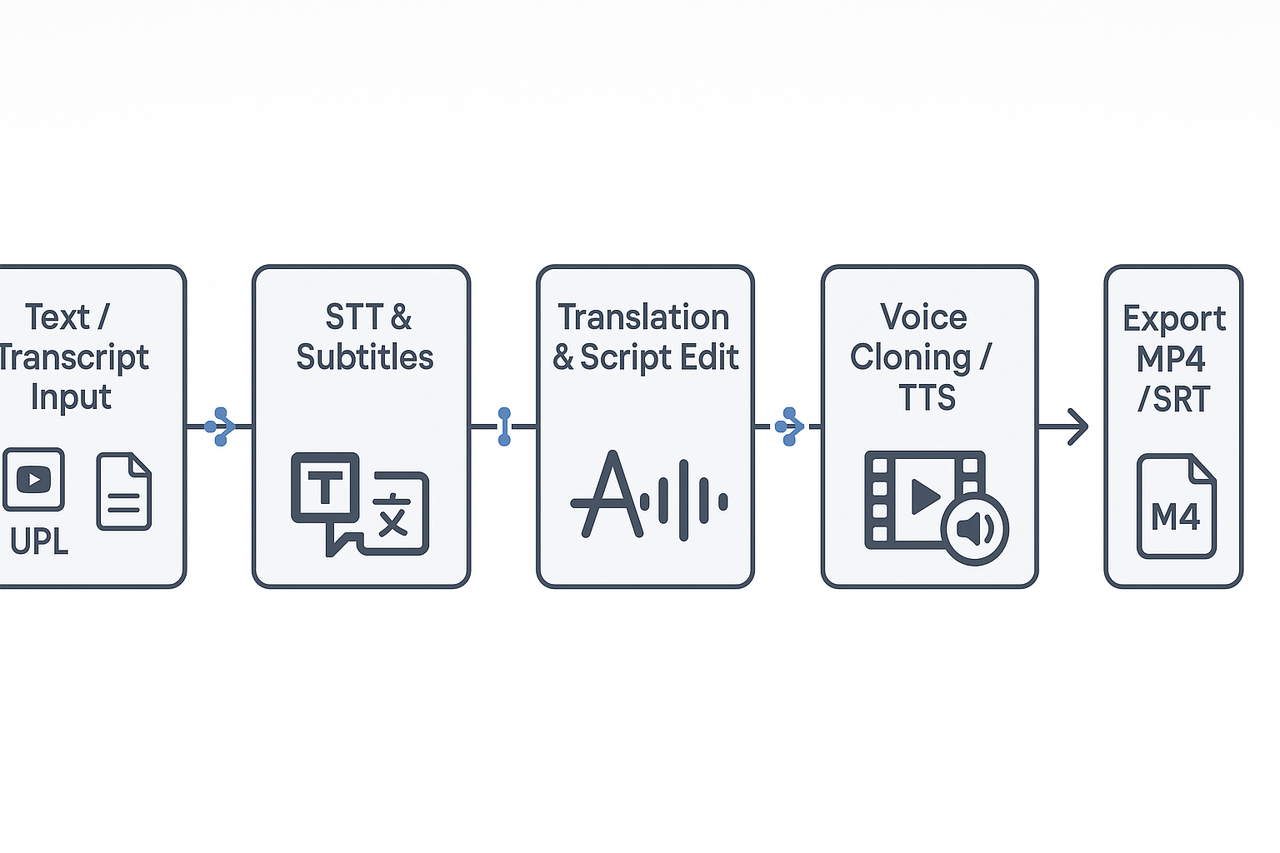
Source transcript and proof (input): use YouTube transcript import or uploaded audio, then run Speech to Text for a clean transcript and timecodes.
-
Auto subtitles and alignment: generate AI subtitles, edit them in-line, and export SRT for captions.
-
Translation and tone pass: translate subtitles or script, then run an AI writing polish pass for idiomatic tone.
-
Voice generation or clone: pick a TTS voice or clone the creator voice for brand consistency, select style and emotion.
-
Dubbing and sync: auto-align dubbed audio to video, apply lip-sync adjustments for talking heads, and preview.
-
Export and publish: export MP4 with embedded audio and burned captions, plus standalone SRT and MP3 files.
Example workflows: solo creator and small team
-
Upload video or paste YouTube URL.
-
Auto-transcribe, run quick subtitle edit, pick 1–2 target languages.
-
Use a high-quality TTS voice for each language, export MP4s and SRTs.
-
Extract transcript, assign human editor to polish translated scripts.
-
Use voice cloning for the creator’s voice for top markets, else premium TTS.
-
Batch-process 5–20 videos using API, review final renders, publish with localized metadata.
Tool Comparison: DupDub vs Alternatives
Quick feature snapshot
|
Feature
|
DupDub (single platform)
|
Mixed-tool stack (specialist apps)
|
|
TTS quality
|
High variety, 700+ voices, many styles
|
Varies by vendor; can be best-in-class for one voice
|
|
Voice cloning
|
Built-in cloning for many languages
|
Often requires a separate vendor and manual sync
|
|
Subtitle alignment
|
Auto alignment and editable subtitles in one timeline
|
Subtitle tools excel, but you must export/import
|
|
API automation
|
Unified API, end-to-end workflow automation
|
Multiple APIs, more integration work
|
|
Workflow speed
|
Fast, fewer handoffs, one export
|
Slower, switching apps creates friction
|
|
Cost to start
|
Predictable, credit-based plans
|
Can be lower per feature, but adds up
|
Pros and cons by team size
-
One interface, faster learning curve.
-
Lower time spent on exports and reformatting.
-
Predictable monthly cost.
-
Slightly less fine-tuned voice for niche needs.
-
Less choices if you want a single boutique voice vendor.
-
Consolidated review cycles, collaboration inside one project.
-
Better subtitle and video sync without manual imports.
-
API and batch jobs scale without extra scripting.
-
May pay for features you rarely use.
-
Very specific audio engineers might prefer dedicated TTS tools.
-
Centralized audit trails and faster turnaround.
-
Easier QA for translated scripts and on-screen text.
-
Automation reduces recurring costs at scale.
-
Large teams with existing pipelines may resist migration.
-
Extreme custom audio workflows can still need specialist tools.
Budgeting & ROI: Cost Estimates for Small, Mid & Large Channels
Realistic cost scenarios: DIY, agency, and DupDub
|
Channel size
|
DIY (freelancers/tools)
|
Agency
|
DupDub (subscription + credits)
|
|
Small (50k views/mo)
|
$$200 to$$500
|
$$700 to$$1,500
|
$$30 to$$150
|
|
Mid (300k views/mo)
|
$$600 to$$1,200
|
$$2,000 to$$4,000
|
$$100 to$$450
|
|
Large (2M views/mo)
|
$$2,000 to$$4,000
|
$$8,000 to$$15,000
|
$$300 to$$1,200
|
Mini ROI examples you can re-run
-
Small channel: 50,000 views, +15 percent = 7,500 extra views, ~$$22.50 monthly revenue. If DupDub runs at$$75/month, payback takes a few months and value grows as languages compound.
-
Mid channel: 300,000 views, +20 percent = 60,000 extra views, ~$$180 monthly. A$$250 monthly localization spend can break even in 1 to 2 months.
-
Large channel: 2,000,000 views, +25 percent = 500,000 extra views, ~$1,500 monthly. Localization costs often pay for themselves within weeks.
DupDub credits and cost saving tips
-
Batch localize several videos at once to save editing time.
-
Prioritize subtitles first, then add dubbed audio for top languages.
-
Reuse voice clones and translated scripts across episodes.
-
Monitor top-performing languages, then scale spend there.
Technical, Legal & Cultural Pitfalls to Avoid
Copyright and fair use risks
Get clear consent for voice cloning
Avoid cultural mistakes that harm trust
Localization QA checklist
-
Verify subtitle accuracy and timing, including proper nouns and numbers.
-
Check on-screen text translations and replace graphics if needed.
-
Match voice tone and pacing to the original intent.
-
Run a native-speaker review for slang and cultural tone.
-
Confirm copyright licenses and license durations.
-
Store consent records for voice talent or clones.
Accessibility rules to prevent compliance issues
-
Always include captions, not just subtitles.
-
Keep captions verbatim for speech, and add speaker labels when needed.
-
Use readable fonts, 16px or larger on mobile.
-
Meet color contrast for text on video.
-
Provide descriptive audio or transcripts for key visual content.
How to Measure Localization Success (KPIs & Analytics)
Primary KPIs to track
-
Watch time: total minutes viewers watch your localized videos. It drives algorithmic reach and monetization. For context, EasyInsights (2025) notes YouTube's Partner Program requires channels to have at least 4,000 total watch hours in the last 365 days to be eligible for monetization, so watch time matters.
-
Retention (average view duration and retention curve): tells if the translation or dub keeps attention. Compare the retention curve of localized vs original videos.
-
Click through rate (CTR): measures thumbnail and title appeal in each language. A low CTR means your translated metadata needs work.
-
Regional subscribers and growth: new subs from target countries show long term audience building.
-
RPM and revenue per region: track RPM (revenue per mille, or per 1000 views) to see if localization raises monetization rates.
How to run A/B tests and set regional attribution
-
Choose one variable: voiceover, subtitle style, thumbnail, or title. Test one change at a time.
-
Segment by region using YouTube Analytics geography filters. Use country or language groups for clearer signals.
-
Run the test long enough, usually 2 to 8 weeks depending on traffic. Aim for at least several hundred to a thousand views per variant for reliable trends.
-
Compare watch time, retention, CTR, and subscriber lift per region. Use YouTube comparisons and export CSV for deeper analysis.
Timelines and benchmarks
-
Small channels under 50k views per month: expect meaningful signals in 6 to 12 weeks.
-
Mid channels: 3 to 6 weeks.
-
Large channels: 1 to 3 weeks.
Starter Checklist & 1‑Week Launch Plan for Creators
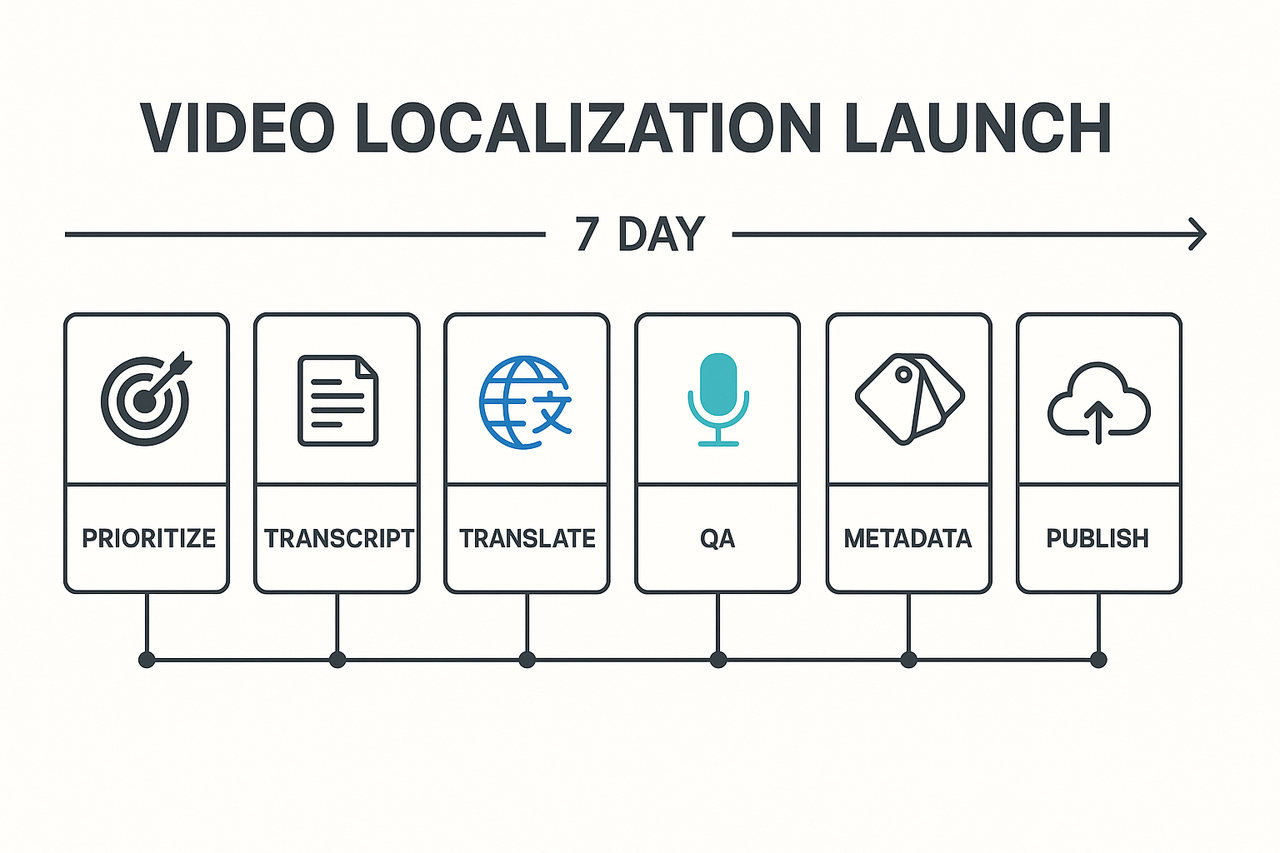
10-step checklist (action-first)
-
Pick the target market and language priorities.
-
Export or generate a clean transcript (captions file like SRT).
-
Review on-screen text and list graphics that need translation.
-
Translate script and on-screen copy, keeping short captions.
-
Do a cultural check for imagery and phrasing.
-
Create localized subtitles and align timings.
-
Produce dubbing: quick AI dub or voice clone for brand voice.
-
Replace on-screen text and render localized cuts.
-
QA watch the full localized edit with native reviewers.
-
Upload, add localized metadata, and schedule publish.
1-week launch plan (daily)
FAQ — Common questions creators ask about video localization
-
Subtitles vs dubbing for YouTube video localization
For video localization for YouTubers, choose subtitles when you want speed and low cost. Subtitles keep the creator's voice and work well for tutorials, interviews, and fast uploads. Dubbing raises production time and cost, but improves watch time in markets that prefer native audio. Mix both: subtitles plus a dubbed version for your top languages.
-
Cost expectations for translation of YouTube video projects
Budget depends on length and quality. Typical ranges: - Small channels: $$10–$$75 per video using automated subtitles and TTS (text-to-speech). - Mid channels: $$75–$$500 per video for human-quality dubbing or hybrid workflows. - Large channels: $500+ for pro voice actors, mixing, and localization QA.
-
How many languages to start with for video localization for YouTubers
Start with 2 to 3 languages tied to real audience signals. Check your YouTube analytics for viewer locations and watch time. Pick languages that cover 60–80 percent of non-English views first. Scale up after you see improved engagement and retention in those markets.
-
Is voice cloning legal for YouTube dubbing and translations
Voice cloning is legal with consent. Always get explicit, documented permission before cloning another person’s voice. If you clone your own voice, keep records, and follow platform policies and local laws. Use tools with privacy controls and encryption to protect voice data.
-
SEO impacts: Does YouTube video localization help discoverability
Yes, localized subtitles and metadata boost search reach in other languages. Translate titles, descriptions, and tags, and upload SRT files to capture non-English searches. Monitor impressions, CTR, and watch time by region to prove ROI. For integrated workflows, consider a platform that handles subtitles, dubbing, and exports in one place, like DupDub.

