-
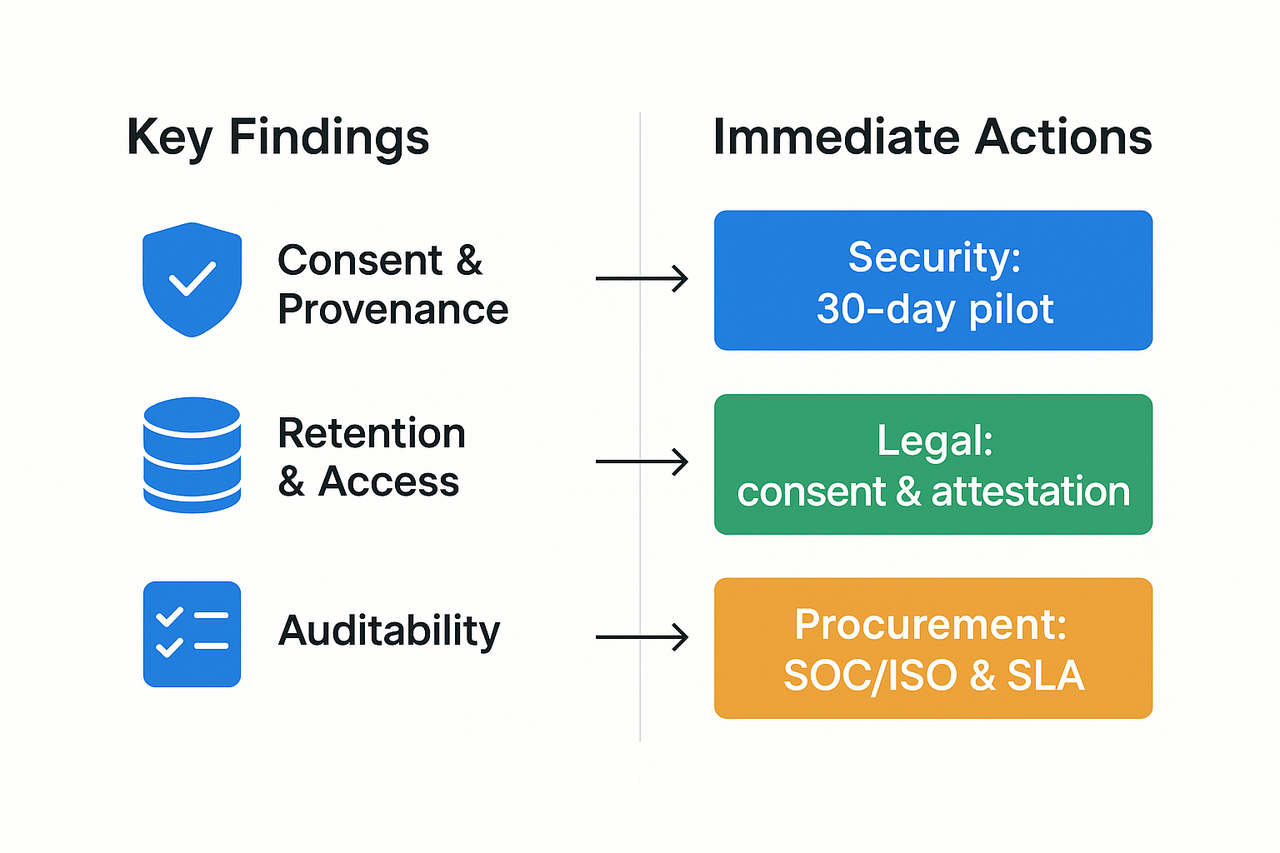
Consent and provenance (origin and usage history): verified speaker consent is often missing, and tamper-resistant provenance logs are rare.
-
Data retention and access: retention policies are vague, and encryption and role-based access controls are inconsistent across vendors.
-
Auditability and vendor assurance: many providers lack third-party audits, clear SLAs, and forensic-friendly logs for incident response.
-
Security: run a 30-day pilot with red-team spoof tests and full log export to validate controls.
-
Legal: require recorded consent, written model-use attestation, and contractual audit rights.
-
Procurement: demand SOC or ISO evidence, data residency options, and incident SLAs.
Why voice cloning needs a corporate risk checklist
What this technology does and why it matters
Common threat patterns enterprises see
-
Credential and payment fraud using cloned executive voices.
-
Social engineering attacks that bypass voice authentication.
-
Brand reputation damage from leaked or misattributed recordings.
-
Regulatory fines are imposed when personal data or biometric voice data lacks proper consent.
Core obligations for consent and data subject rights
-
Capture and log explicit consent with purpose text and timestamp.
-
Limit retention, and auto-delete voice samples after the stated purpose.
-
Encrypt data at rest and in transit, and isolate voice models per user.
-
Provide simple user controls for access, deletion, and portability.
Sector-specific priorities: finance, healthcare, telecom
-
Finance: Prevent fraud, keep immutable logs, and restrict cloning for transaction approval.
-
Healthcare: Treat voice as health data where local law applies, and require strict medical-data safeguards.
-
Telecom: Protect metadata and location signals, block unauthorized retransmission and spoofing.
Practical procurement checklist for cross-border processing
-
Require Data Processing Agreements with clear subprocessors and audit rights.
-
Demand DPIAs (data protection impact assessments) for high-risk cloning projects.
-
Insist on regional data residency options and documented transfer mechanisms.
-
Verify that models are voice-locked to the original speaker and that raw samples are not reused.
-
Require breach notification SLAs, deletion proofs, and routine third-party security reviews.
Regulatory & privacy landscape for synthetic voice
Core legal principles to map
-
Consent capture and tamper-proof logs.
-
Short, documented retention periods and deletion automation.
-
Pseudonymization or encryption for stored samples.
-
Purpose limitation: no reuse without new approval.
-
DPIA (data protection impact assessment) completed before launch.
Sector-specific priorities: finance, healthcare, telecom
Practical implications for procurement teams
-
DPIA and threat model validated.
-
Signed data processing agreement with clear roles.
-
Automated retention and delete-by-request mechanisms.
-
Technical attestations for anti-spoofing and logging.
Governance and policy
-
Requirement: Formal policy, roles, and risk register for synthetic voice. Align controls to an ISMS. For governance, require an ISMS aligned to ISO/IEC 27001:2022 - Information security management systems, and document owner duties and review cycles.
-
Pass/fail: Pass if policy, owner, and review cadence exist and are documented. Fail if policy is absent or unowned.
-
Ask for: policy PDF, risk register excerpt, and recent board minutes.
-
Map to product: confirm vendors support consent logging, tenant isolation, and enterprise contracts. Higher tiers often include contractual SLAs and enterprise review windows.
Data collection and storage
-
Requirement: Explicit consent records, minimal data collection, encryption in transit and at rest, and stated retention limits.
-
Pass/fail: Pass if vendor stores consent records and encrypts data. Fail if voice samples or keys are reused without consent.
-
Ask for: data flow diagram, encryption algorithms, and data retention policy.
-
Map to product: verify "voice cloning locked to original speaker" and encrypted processing. Check which pricing tier includes secure storage and larger retention.
Model provenance and controls
-
Requirement: Training data lineage, ability to opt out, synthetic watermarking, and provenance logs.
-
Pass/fail: Pass if the vendor provides provenance logs and detection tools. Fail if they cannot trace model updates or training sources.
-
Ask for: model change log, dataset summaries, and watermarking or detectable signature method.
-
Map to product: request API access to provenance records and any available watermarking features.
Access controls and cryptography
-
Requirement: Role-based access, SSO, MFA, API key policies, key rotation, and cloud KMS.
-
Pass/fail: Pass if SSO and MFA are enforced for admin roles. Fail if shared credentials or no rotation policy exist.
-
Ask for: auth architecture, access matrix, and key management evidence.
Monitoring, detection, and third-party due diligence
-
Requirement: Audit logs, anomaly detection, incident response plan, subprocessors list, and periodic audits.
-
Pass/fail: Pass if logs are available, a label, and an IR SLA exists. Fail if no logging or no subprocessor disclosure.
-
Ask for: sample audit log, SOC or penetration test report, and DPA with subprocessor list.
Technical integration & implementation steps for IT teams
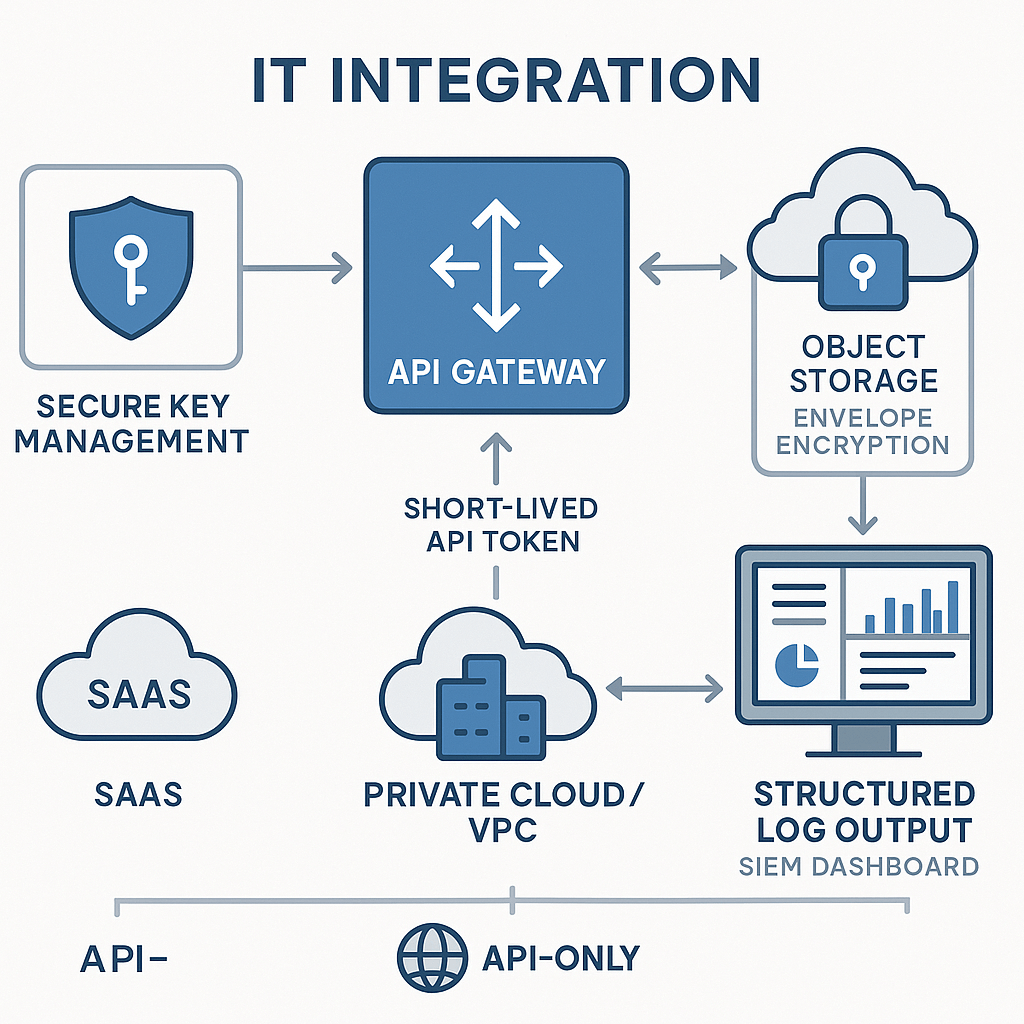
Secure keys and encryption: keep credentials short-lived
Logging and observability: what to send to SIEM
Deployment models and API patterns
Implementation checklist for engineering (ordered)
-
Define threat model and data flow diagram.
-
Provision vault-based key rotation and RBAC.
-
Enforce TLS, strong cipher suites, and envelope encryption.
-
Implement structured logging and SIEM ingestion.
-
Add consent capture and immutable audit records.
-
Run end-to-end tests for latency and failure modes.
Measuring effectiveness: KPIs and audit metrics
Track these KPIs
-
Operational uptime, the percent of time services are healthy.
-
End-to-end latency, median, and 95th percentile in milliseconds.
-
Throughput, requests processed per minute, and peak capacity.
-
Processing time per clone, average seconds per job.
-
Detection accuracy, track precision, and recall (detection tradeoffs explained).
-
False positive rate, percent of benign audio flagged incorrectly.
-
Spoof detection rate, successful blocks of synthetic attacks.
-
Consent capture rate, percent of cloned voices with signed consent.
-
Audit coverage, percent of audible outputs logged, and traceability.
-
Time to remediate, median hours from detection to fix.
Audit evidence and reporting cadence
Addressing ethical concerns & employee impact
Consent, training, and morale
Policy language and whistleblowing channels
Where DupDub fits: vendor comparison and pricing alignment
Map controls to plan levels
|
Control
|
DupDub plan mapping
|
Typical competitor expectation (ElevenLabs, Murf, Play.ht)
|
|
Encryption in transit and at rest
|
Included across Paid plans; verify key handling on Ultimate
|
Paid plans, enterprise tiers often required
|
|
Voice cloning consent & provenance (speaker lock)
|
Core voice lock feature; confirm retention policy on Pro/Ultimate
|
Offered, but ask for provenance workflow and consent logs
|
|
API access, rate limits, and audit logs
|
API on Professional+; Ultimate for higher quotas and retention
|
API on paid tiers; enterprise plans for long log retention
|
Evidence to request during security review
-
SOC 2 or ISO attestation, or roadmap for audit completion.
-
Data flow diagram showing where audio and clones are stored.
-
Encryption details: algorithms, key management, and customer key options.
-
Consent and provenance logs showing how clones are created and bound to originals.
-
Retention and deletion policy for voice models and raw samples.
-
Demo of admin controls, RBAC (role-based access control), and audit trails.
FAQ — common legal, technical, and procurement questions
-
How do we run a voice-based risk assessment during vendor review?
Start with a short checklist: verify consent capture, map data flows, confirm encryption at rest and in transit, and require a DPIA (data protection impact assessment) for high-risk use. Ask for sample deletion and model-lock guarantees.
-
What consent logging for voice cloning should we require?
Require recorded explicit consent, timestamped logs, linked user ID, and retention policies. Store immutable hashes of audio samples and consent forms for audits.
-
Which auditor KPIs for synthetic voice should we track?
Track consent coverage, number of deleted models, false positive misuse alerts, mean time to remediate, and frequency of third-party audits.
-
Are cloned voices reversible or deletable on demand?
Require the vendor to delete voice models and derived data on request, confirm deletion proofs, and set SLA timelines for removal.
-
When to escalate to legal or privacy teams for voice cloning?
Escalate for celebrity likeness, cross-border transfers, law enforcement requests, or DPIA findings showing high residual risk.
-
What procurement clauses for voice cloning vendors are essential?
Include DPA, security SLA, breach notification timelines, subprocessor disclosure, and indemnity for misuse.
-
What technical blockers delay deployment and integration?
Low-quality samples, missing APIs, key management gaps, and inadequate logging are common blockers. Plan a short pilot to validate the end-to-end flow.

